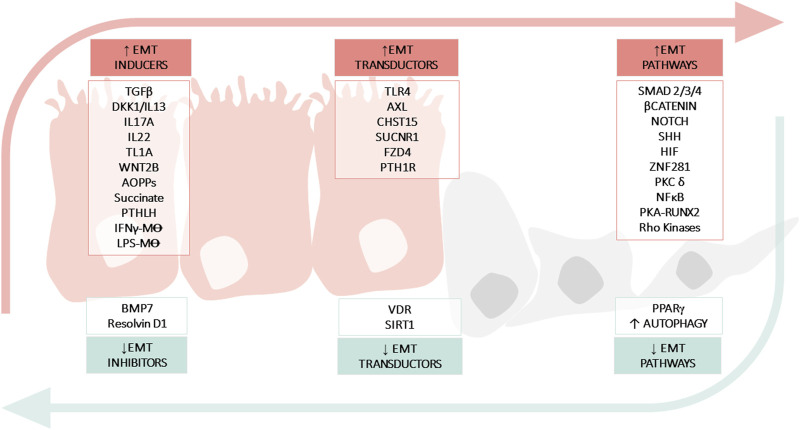
FIGURE 2.
Molecular mechanisms implicated in epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in IBD. The figure shows: soluble molecules, cells or hormones related with the induction (INDUCERS) or inhibition (INHIBITORS) of the EMT process; receptors or enzymes implicated in the EMT process (TRANSDUCTORS) and pathways related with EMT (PATHWAYS). Advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs); Bone morphogenic protein-7 (BMP7); Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 15 (CHST15); Crohn’s Disease (CD); Dickkopf-homolog-1 (DKK1); Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF); Inflammatory Bowel disease (IBD); Interferon (IFN); Interleukin (IL); Lipopolysaccharide (LPS); Macrophage (M⊝); Nuclear Factor kB (NFκB); Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); Parathyroid hormone-like hormone (PTHLH); Parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTH1R); Protein kinase (PK); Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARγ); Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2); Silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1); Sonic Hedgehog (SHH); Transforming growth factor (TGF); Tumour necrosis factor-like ligand 1A (TL1A); Ulcerative Colitis (UC); Vitamin D receptor (VDR); Zinc-finger E-box-binding (ZEB).