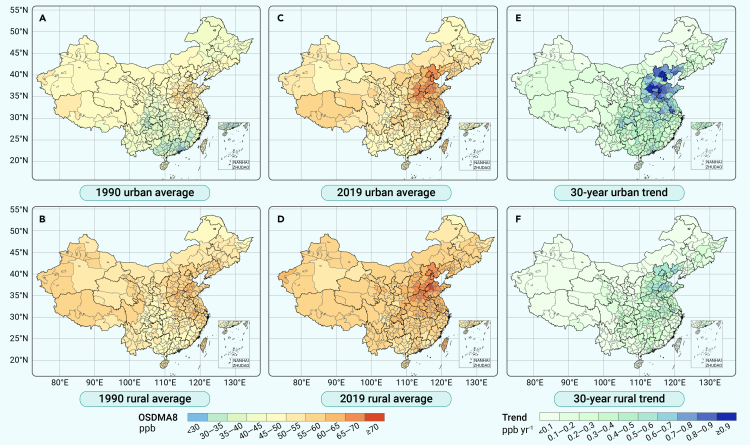
Figure 1.
Mapping of prefecture-city-level ambient ozone and temporal trends
(A and B) Peak ambient ozone concentrations with urban-rural differentiation for 1990 by metric of 6-month (April to September) ozone-season daily 8-h maximum average (OSDMA8, ppb).
(C and D) Peak ambient ozone concentrations for 2019 by OSDMA8.
(E and F) Thirty-year annual average change rates. Upper panels (A, C, and E) are distinguished for urban residential environments, and lower panels (B, D, and F) for rural living environments. Ambient ozone concentrations in 10-km spatial resolution are predicted by fusion of multiple downscaled data products (see Methods S1 and S2) and are averaged for mapping in prefecture-level cities. Urban and rural temporal change rates for each prefectural city are estimated by generalized linear model. Province-level statistics for 1990 and 2019 are listed in Table S1. Base-map of China credits to Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC.