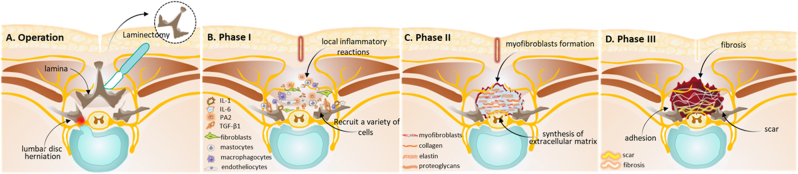
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram illustrating the development of epidural fibrosis after lumbar spinal laminectomy (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the laminectomy surgery for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation (B) The development of epidural fibrosis can be divided into three phases. Phase I involves local inflammatory reactions which occur in the first 3 to 5 postoperative days (C) Phase II is the active phase of fibroblasts which usually lasts 2–3 weeks after surgery. In this phase, fibroblasts proliferate and differentiate into myofibroblasts which are the chief perpetrators of fibrosis and avid extracellular matrix synthesizers (D) Phase III involves tissue reconstruction which lasts for months or longer. Epidural fibrosis and scar tissue form during this phase which may cause CPSS and functional incapacity. IL-1, interleukin-1; IL-6, interleukin-6. PA2; phospholipase A2; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1.