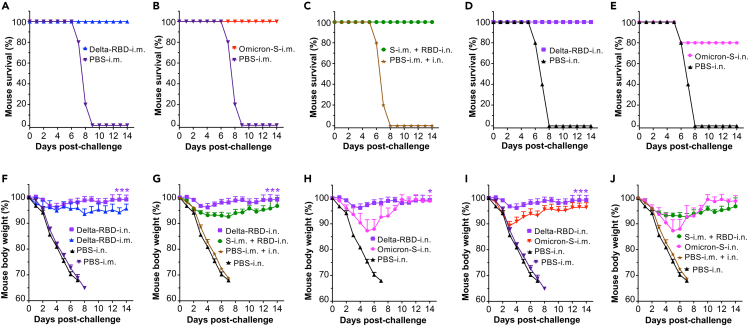
Figure 5.
Intranasally immunized Delta-RBD protein with or without Omicron-S priming protected mice from challenge with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant
One month after the last immunization of the respective vaccines or PBS control plus adjuvant(s), K18-hACE2 mice were challenged with a SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (104 PFU/mouse), and mouse survival and weight changes were investigated for 14 days post-challenge.
(A–E) Survival of challenged mice immunized with Delta-RBD-i.m. (A), Omicron-S-i.m. (B), S-i.m. + RBD-i.n. (C), Delta-RBD-i.n. (D), or Omicron-S-i.n. (E).
(F–J) Comparison of weight changes of challenged mice immunized with Delta-RBD-i.n. or Delta-RBD-i.m. (F), Delta-RBD-i.n. or S-i.m. + RBD-i.n. (G), Delta-RBD-i.n. or Omicron-S-i.n. (H), Delta-RBD-i.n. or Omicron-S-i.m. (I), and S-i.m. + RBD-i.n. or Omicron-S-i.n. (J), respectively.
The data (in F–J) are shown as mean +s.e.m. of five mice in each group. Delta-RBD-i.m. or Delta-RBD-i.n. indicates Delta-RBD protein intramuscular or intranasal immunization. Omicron-S-i.m. or Omicron-S-i.n. indicates Omicron-S protein intramuscular or intranasal immunization. S-i.m. + RBD-i.n. indicates i.m. priming with the Omicron-S protein followed by i.n. boosting with the Delta-RBD protein. Controls, PBS with relevant adjuvants injected via i.m., i.m. + i.n., or i.n. route. ∗ (p < 0.05) and ∗∗∗ (p < 0.001) designate significant differences among Delta-RBD-i.n. and other groups.