Abstract
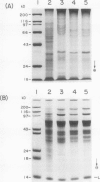
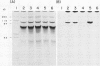
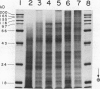
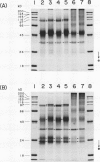
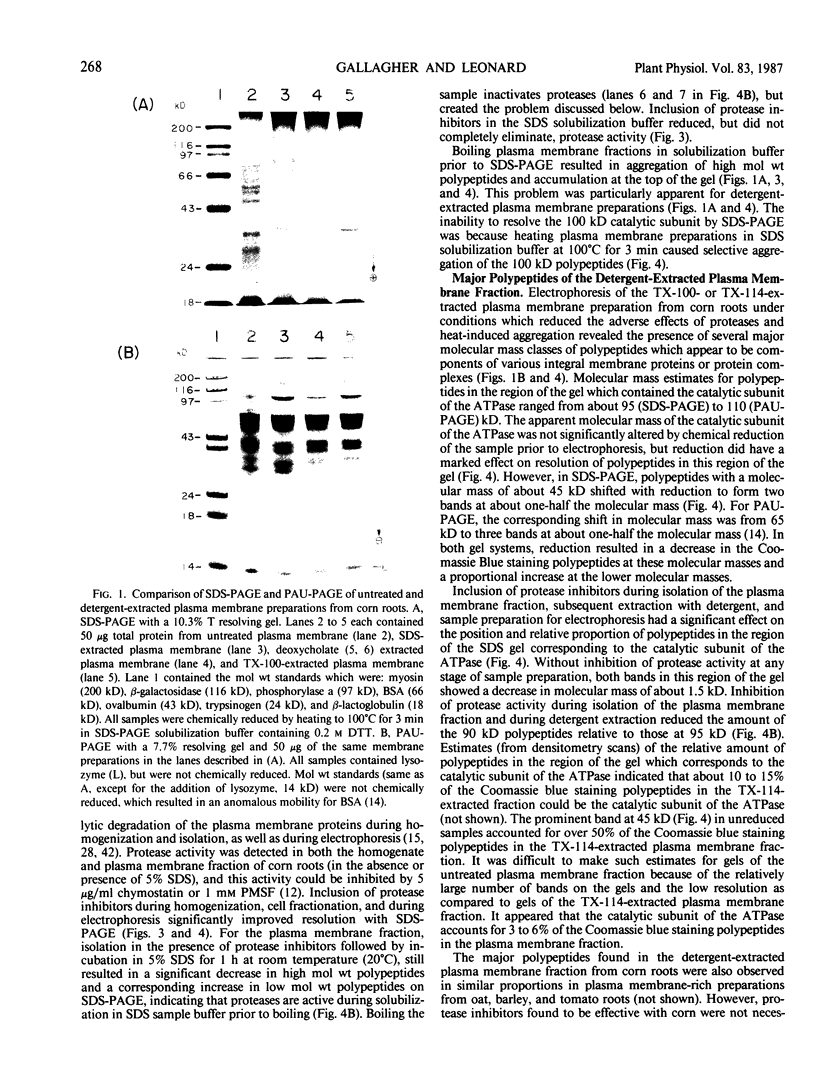
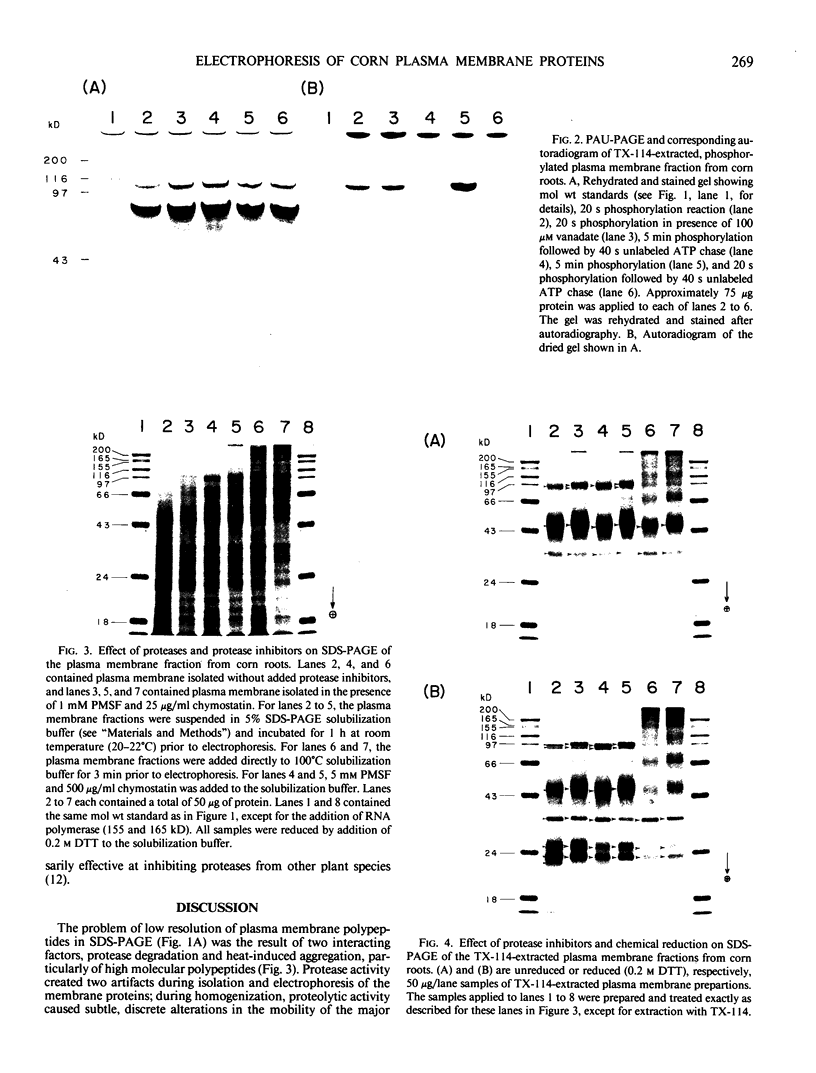
Experiments were conducted to determine conditions essential for electrophoretic characterization of a detergent-extracted plasma membrane fraction from corn (Zea mays L.) roots. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) initially gave poor resolution of polypeptides in the plasma membrane fraction and, upon detergent treatment for purification of the proton-pumping adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), showed no enrichment for a 100 kilodalton catalytic subunit characteristic of the ATPase. In contrast to SDS-PAGE, phenol urea acetic acid (PAU)-PAGE clearly resolved two polypeptides in the 100 kilodalton region that were enriched during detergent treatment and indicated at least one polypeptide forms a phosphorylated intermediate characteristic of the ATPase. Problems with SDS-PAGE were found to be caused, in part, by a combination of endogenous proteases and heat-induced aggregation of high molecular weight proteins. The usually standard procedure of boiling the sample prior to SDS-PAGE caused the aggregation of the 100 kilodalton polypeptides. By controlling for proteases using chymostatin and/or phenylmethane sulfonyl floride, and not boiling the sample prior to electrophoresis, two polypeptides were clearly resolved by SDS-PAGE in the 100 kilodalton region of Triton X-114-extracted membranes from corn, oat, barley, and tomato.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison R., Scarborough G. A. Solubilization and purification of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13165–13171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthon G. E., Spanswick R. M. Purification and properties of the h-translocating ATPase from the plasma membrane of tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booz M. L., Travis R. L. Electrophoretic comparison of polypeptides from enriched plasma membrane fractions from developing soybean roots. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1037–1043. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Partial characterization of a phosphorylated intermediate associated with the plasma membrane ATPase of corn roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Phosphorylation of the adenosine triphosphatase in a deoxycholate-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1459–1464. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Plasma membrane ATPase of red beet forms a phosphorylated intermediate. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):507–512. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Thornley W. R., Roti-Roti J. L. Target molecular size of the red beet plasma membrane ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jul;78(3):642–644. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.3.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Leonard R. T. Solubilization and partial purification of the adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):931–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Carroll E. J., Leonard R. T. A sensitive diffusion plate assay for screening inhibitors of protease activity in plant cell fractions. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):869–874. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M., Chrambach A. Solubilization of functional membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:305–318. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. M., Melhado L. L., Ho T. H., Pearce C. J., Leonard N. J. Azido auxins : photoaffinity labeling of auxin-binding proteins in maize coleoptile with tritiated 5-azidoindole-3-acetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1111–1116. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Mechanism of the Na+, K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):27–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamo K. Purification and Properties of the Plasma Membrane H-Translocating Adenosine Triphosphatase of Phaseolus mungo L. Roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):818–824. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Robson R. J., Dennis E. A. Solubilization of phospholipids by detergents. Structural and kinetic aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):285–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Serrano R. Purification of the yeast plasma membrane ATPase solubilized with a novel zwitterionic detergent. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80763-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morré D. J., Morré J. T., Varnold R. L. Phosphorylation of membrane-located proteins of soybean in vitro and response to auxin. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):265–268. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R. Methods for avoiding proteolytic artefacts in studies of enzymes and other proteins from yeasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:149–184. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60956-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Ruesink A. W. Orientation and integrity of plasma membrane vesicles obtained from carrot protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):385–391. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalla R., Amory A., Rigaud J., Goffeau A. Phosphorylated intermediate of a transport ATPase and activity of protein kinase in membranes from corn roots. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Plasma membrane ATPase of fungi and plants as a novel type of proton pump. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:87–126. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152823-2.50007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Purification of the proton pumping ATPase from plant plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation, and difference in affinity for strophanthidin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6060–6067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Partial purification and properties of the proton-translocating ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Phosphorylated intermediate of the ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5334–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Calcium- and calmodulin-regulated phosphorylation of soluble and membrane proteins from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):359–365. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderhaug M. O., Post R. L., Saccomani G., Leonard R. T., Briskin D. P. Structural relatedness of three ion-transport adenosine triphosphatases around their active sites of phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3852–3859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. S., Wang M. Y. Extraction of proteins for sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis from protease-rich plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 15;139(1):100–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90394-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler W. L. Analytical polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and molecular weight determination. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:70–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Renswoude J., Kempf C. Purification of integral membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:329–339. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]