FIGURE 3.
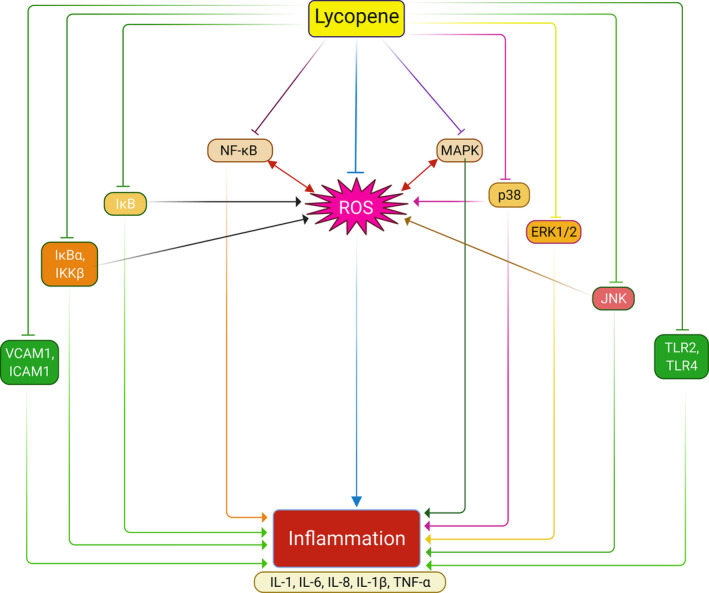
Anti‐inflammatory mechanism of lycopene. Lycopene inhibits inflammation by reducing ROS generation and inflammatory mediators. Primarily, lycopene inhibits ROS production, which plays an interchangeable role in proinflammatory cytokines, including IL‐1, IL‐6, IL‐8, IL‐1β, and TNF‐α release. In addition, lycopene inhibits the MAPK pathway and its isomers p38, ERK1/2, and JNK pathways, subsequently leading to ROS generation and proinflammatory cytokines releases. Similarly, lycopene suppressed phosphorylation of IκB and its phosphorylates IκBα and IKKβ and subsequent activation of the NF‐κB pathway. In addition, lycopene prevents inflammation by inhibiting toll‐like receptors TLR2 and TLR4 and endothelial adhesion molecules VCAM1 and ICAM‐1.
