Figure 3-10.
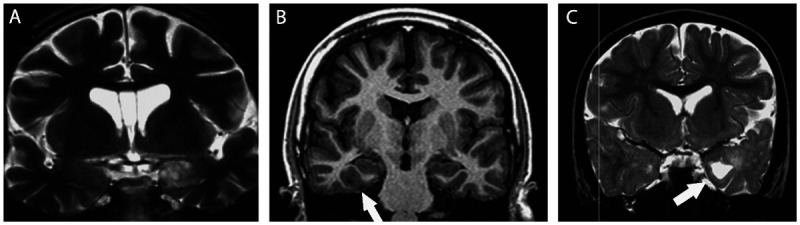
Coronal MRIs showing ganglioglioma in three patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and seizures not responding to antiepileptic drugs who became seizure free after surgical resection of the lesion. A,T2-weighted image showing a ganglioglioma in the left amygdala. B, T1-inversion recovery image showing a small ganglioglioma in the right collateral sulcus (arrow) that was previously missed in an MRI without thin coronal cuts. C, T2-weighted image showing a ganglioglioma in the left uncal region with a cystic component (arrow). Gangliogliomas usually have clear limits and are hypointense on T1 (not shown in this figure) and hyperintense on T2-weighted images. The contrast enhancement is variable from absent to intense, and may present with an annular (ring-enhancing) pattern. Gangliogliomas should be considered when a poorly defined, slightly enhancing mass is present in the temporal lobes.
