Figure 2: Ubiquitous in vivo RNA targeting using a two-component CasRx system (reprinted5).
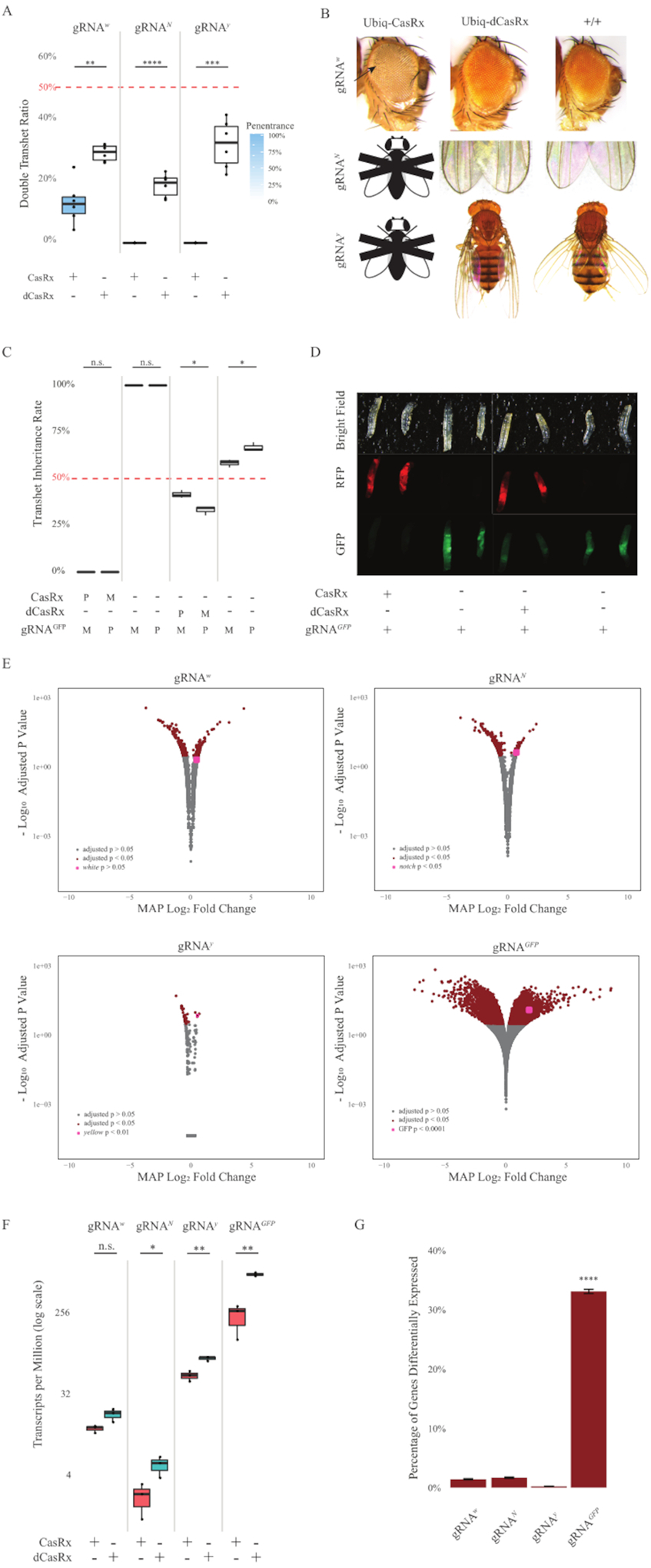
(A) Total inheritance percentages of transheterozygous flies inheriting Ubiq-CasRx (or Ubiq-dCasRx) and gRNAs. Blue shading in the box plot indicates phenotype penetrance. (B) Phenotypes of transheterozygous flies. Arrows indicate tissue necrosis in the eye. Black and white fly marked with “X” represents lethality. (C) Total inheritance percentages of transheterozygous flies of bidirectional crosses between Ubiq-CasRx (or Ubiq-dCasRx) and gRNAGFP-OpIE2-GFP flies. M, maternal inheritance of CasRx; P, paternal inheritance of CasRx. (D) F1 larvae progenies in the paternal cross. (E) Transcripts’ maximum a posteriori estimates for the logarithmic fold change. DESeq2 pipeline was used. (F) Transcripts per million (TPM) targeted with CasRx or dCasRx. (G) CasRx-depentent differentially expressed transcript percentage of transcripts.
