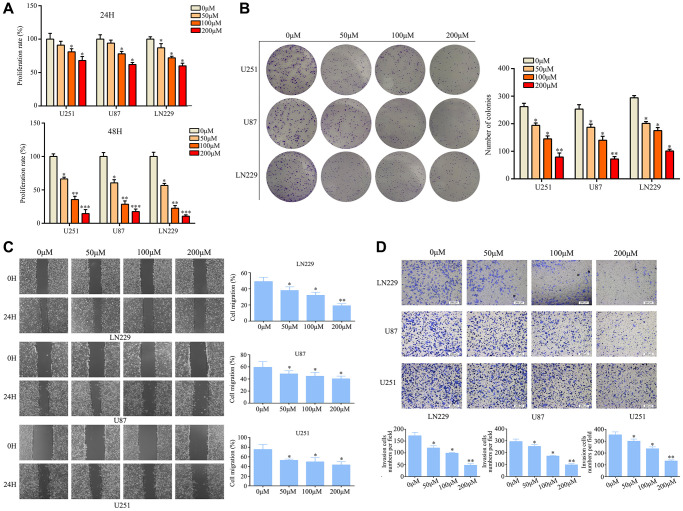
Figure 1.
Ar-turmerone inhibited glioma cell proliferation and mobility in vitro. (A) U251, U87 and LN229 cells were treated with different concentrations of ar-turmerone (0, 50, 100 and 200 μM), and a CCK−8 assay was used to detect the proliferation rate of each group. (B) A colony formation assay was used to detect the colony formation of glioma cells treated with different concentrations of ar-turmerone (0, 50, 100 and 200 μM). (C) A wound healing assay was used to detect the migration of glioma cells treated with different concentrations of ar-turmerone (0, 50, 100 and 200 μM). (D) A Transwell assay was used to detect the invasion of glioma cells treated with different concentrations of ar-turmerone (0, 50, 100 and 200 μM). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.