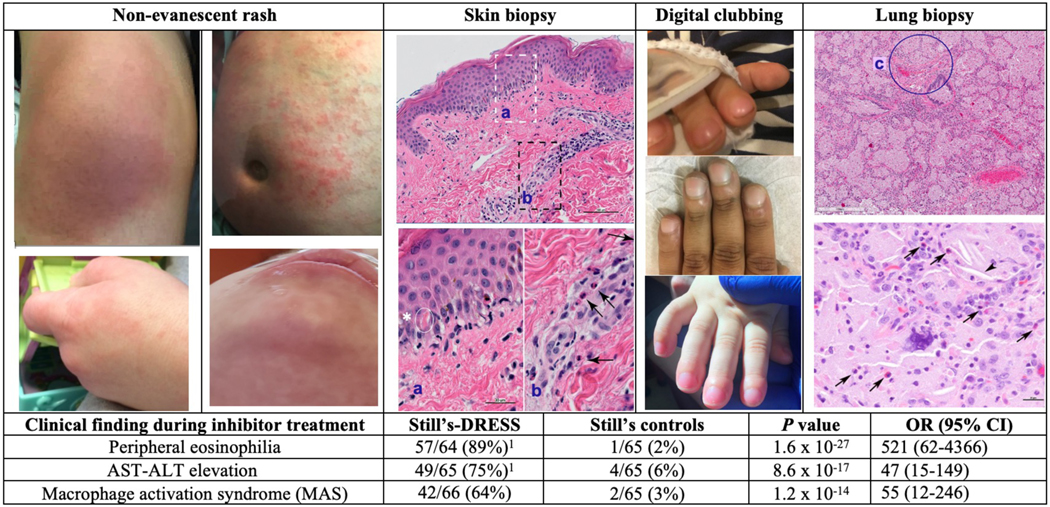
Figure 3: Unusual clinical features in inhibitor-treated Still’s patients.
Images of non-evanescent rash, typically pruritic, are shown. Upper left: On anakinra, erythema and prominent edema affecting knee; upper right: on tocilizumab, excoriated and areas of hyperpigmentation on abdomen; lower left: On canakinumab, erythematous, edematous rash on hand [similar rash on face and ear is not shown]; lower right: On anakinra, erythema, edema and non-herpetic vesiculation on face. Skin biopsy of drug-associated rash shows vacuolar interface dermatitis and eosinophils. Higher power images (sections a, b) show lymphocytes, vacuolation at the dermal-epidermal junction, focal dyskeratotic keratinocytes (asterisk) and perivascular eosinophils (arrows). Acute digital clubbing, often erythematous, was frequently the first indication of lung involvement in patients with DRESS and diffuse lung disease. Images of acute clubbing on tocilizumab (top), anakinra (middle), on canakinumab (bottom). Lung biopsy showing variant pulmonary alveolar proteinosis/endogenous lipoid pneumonia and arterial wall thickening (c). Higher power image (below) shows cholesterol clefts (arrowhead) and scattered eosinophils (arrows). 8/16 reviewed cases showed eosinophils in many fields (see supplementary methods). Increased lung eosinophils are consistent with DRESS and also seen in various inflammatory diseases. Table: In DRESS cases, median (interquartile range) of peak absolute eosinophil count was 1500/ul (980,3080) and peak eosinophil % of WBC was 18% (12,33). AST-ALT elevation was defined as aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) measuring >2x the upper limit of normal more than once, without alternative (e.g., non-drug) explanation. The frequency of DRESS reactions did not differ significantly when combined anti-IL-1 inhibitors were compared to the IL-6 inhibitor (tocilizumab) or when each inhibitor was analyzed separately (table S1c). Analyses of specific clinical findings yielded similar results when AOSD patients were omitted (table S5). See supplementary information for detailed methods and additional clinical data (tables S1c, S2, S3a–b).
DRESS, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; MAS, macrophage activation syndrome, a form of secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis22,23; P value, by Fisher’s exact; OR (95% CI), odds ratio (95% confidence interval)
1Eosinophil information was unavailable in 2 cases (n=64); AST-ALT values were unavailable in 1 case, (n=65).