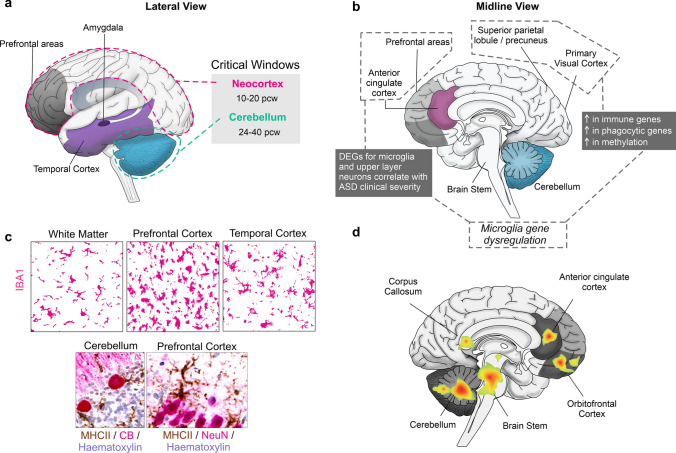
Fig. 2.
Microglial findings in ASCs. a Lateral view of the human brain with the critical/sensitive windows for ASC development, which include the cerebellum and the neocortex [209]. b Microglial gene dysregulation observed in ASC samples from the prefrontal and cingulate [203] as well as the primary visual areas and the superior parietal lobule [49]. c Microglial densities (IBA1+, magenta) are unchanged, higher, or lower in these brain areas compared to typically developing controls (top panel). In the cerebellum and neocortex, neuroinflammatory processes are heightened and microglia express MHC-II (brown) and cup Purkinje Calbindin+ cells in the cerebellum (CB+, magenta) and neurons in the neocortex (NeuN+, magenta) (bottom panel). Scale bars: 25 μm. d Areas of the brain demonstrated to show hyperactivation linked to microglial TPSO signal. Most areas show hyperactivation except the cerebellum and the cingulate which show both hyper and hypoactivation depending on the study [175, 187, 223]