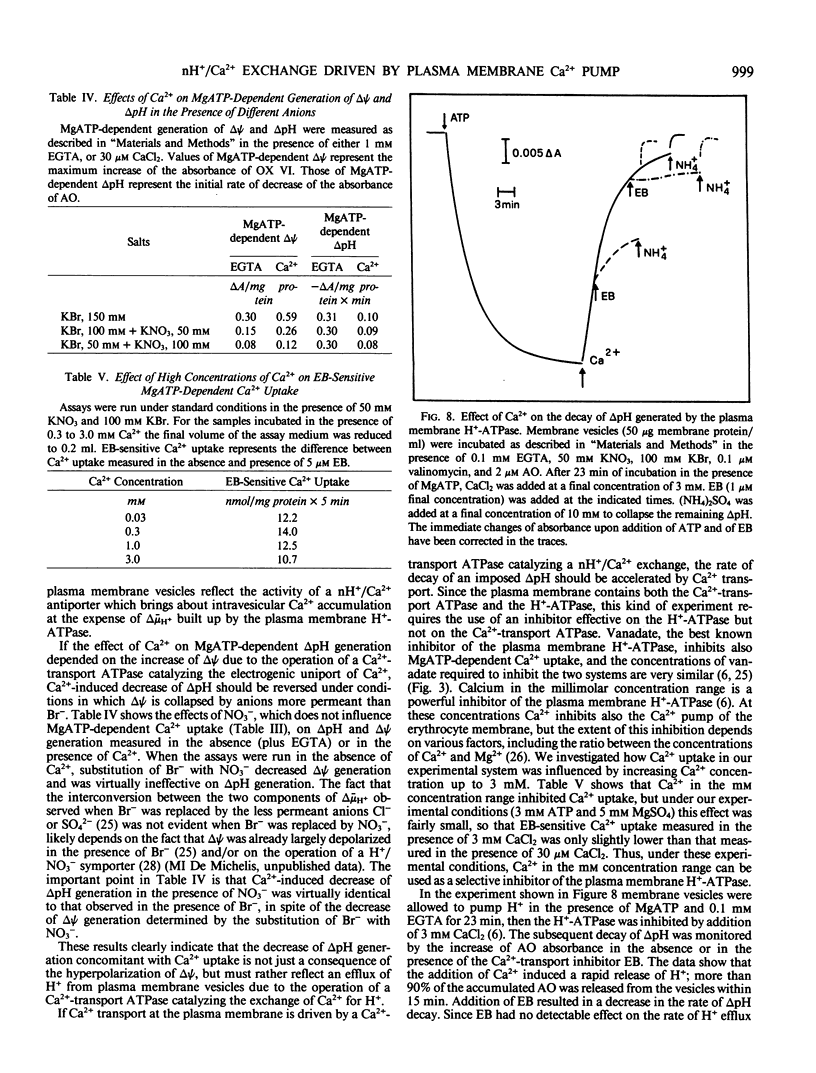
Abstract
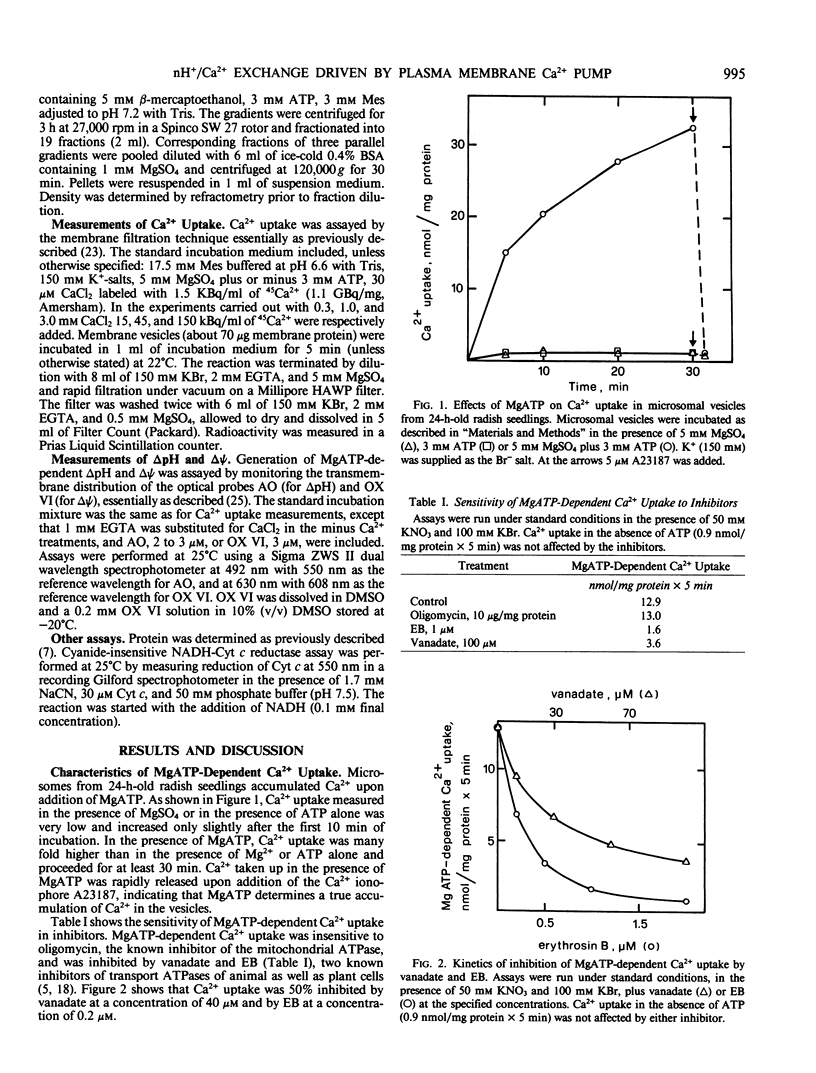
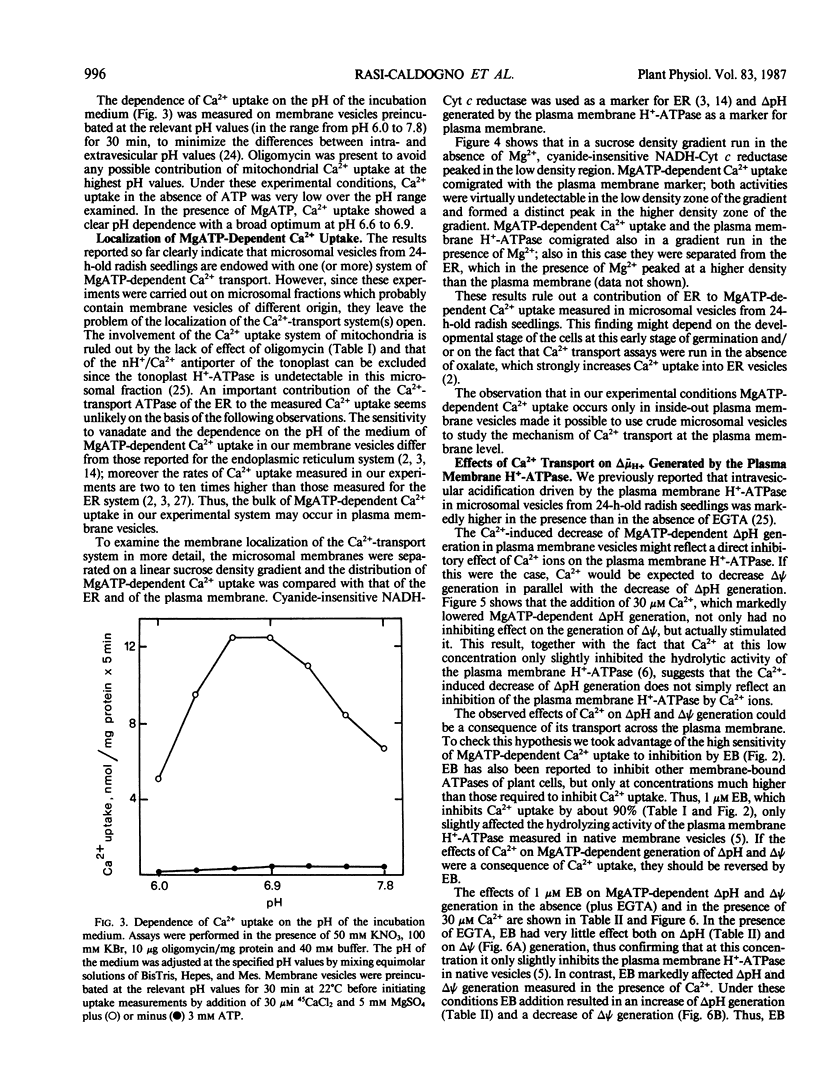
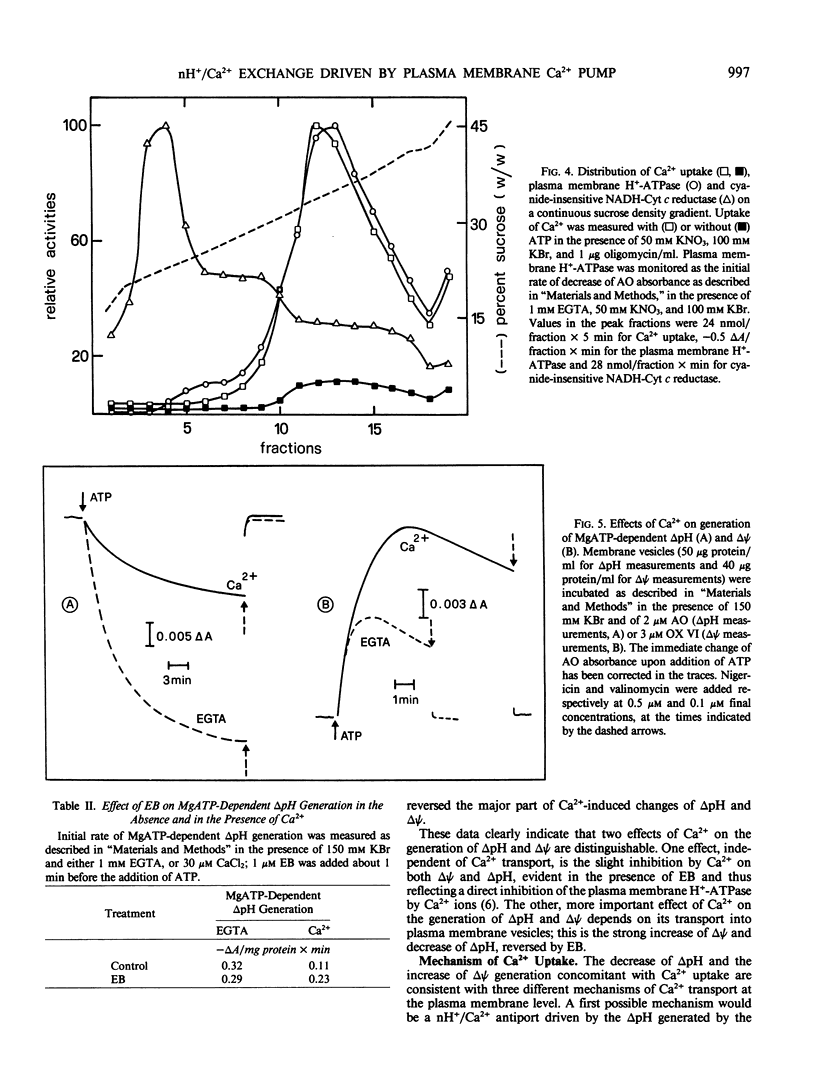
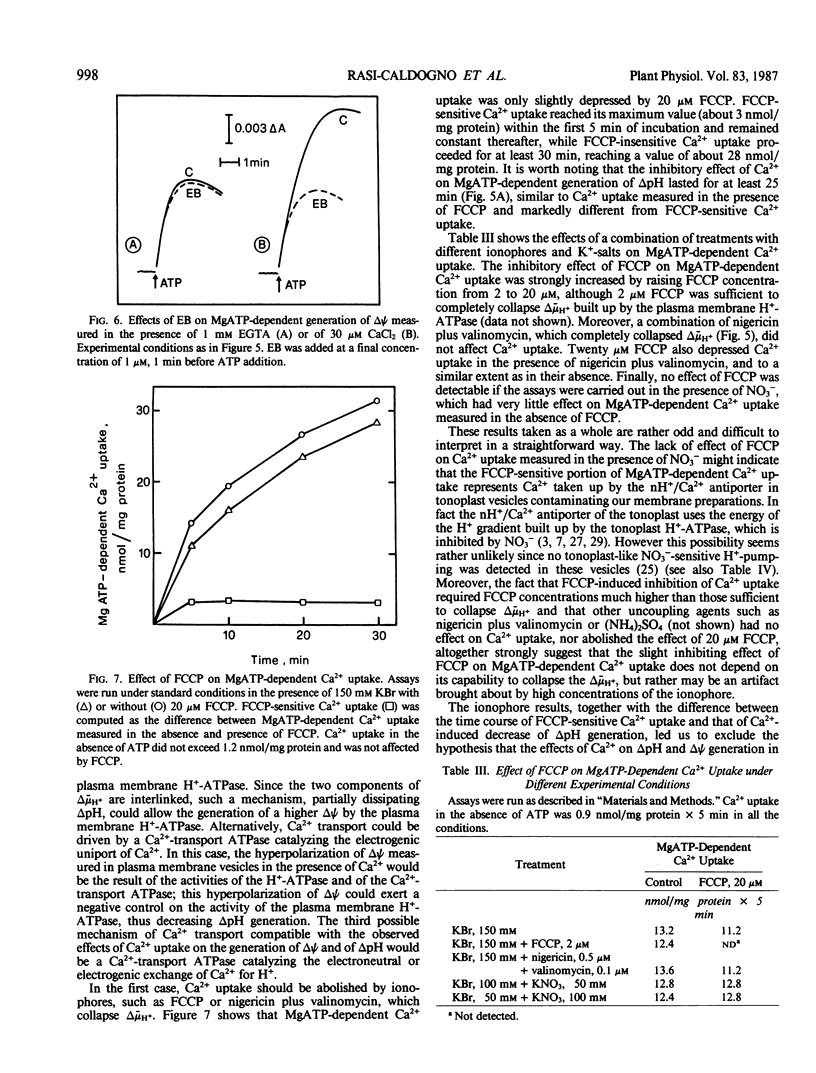
Microsomal vesicles from 24-hour-old radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings accumulate Ca2+ upon addition of MgATP. MgATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake co-migrates with the plasma membrane H+-ATPase on a sucrose gradient. Ca2+ uptake is insensitive to oligomycin, inhibited by vanadate (IC50 40 micromolar) and erythrosin B (IC50 0.2 micromolar) and displays a pH optimum between pH 6.6 and 6.9. MgATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake is insensitive to protonophores. These results indicate that Ca2+ transport in these microsomal vesicles is catalyzed by a Mg2+-dependent ATPase localized on the plasma membrane. Ca2+ strongly reduces ΔpH generation by the plasma membrane H+-ATPase and increases MgATP-dependent membrane potential difference (Δψ) generation. These effects of Ca2+ on ΔpH and Δψ generation are drastically reduced by micromolar erythrosin B, indicating that they are primarily a consequence of Ca2+ uptake into plasma membrane vesicles. The Ca2+-induced increase of Δψ is collapsed by permeant anions, which do not affect Ca2+-induced decrease of ΔpH generation by the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. The rate of decay of MgATP-dependent ΔpH, upon inhibition of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase, is accelerated by MgATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake, indicating that the decrease of ΔpH generation induced by Ca2+ reflects the efflux of H+ coupled to Ca2+ uptake into plasma membrane vesicles. It is therefore proposed that Ca2+ transport at the plasma membrane is mediated by a Mg2+-dependent ATPase which catalyzes a nH+/Ca2+ exchange.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Kinetics of Ca/H Antiport in Isolated Tonoplast Vesicles from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):727–731. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. R., Sze H. Calcium transport in tonoplast and endoplasmic reticulum vesicles isolated from cultured carrot cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):549–555. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Inesi G. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate dependent fluxes of manganese and and hydrogen ions in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2912–2918. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieter P., Marmé D. Calmodulin activation of plant microsomal Ca uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7311–7314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Hanson J. B. Calcium Accumulation by Maize Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jan;40(1):101–109. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimber A., Sze H. Helminthosporium maydis T Toxin Decreased Calcium Transport into Mitochondria of Susceptible Corn. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):804–809. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R. R., Briskin D. P., Wyse R. E. Ca uptake by endoplasmic reticulum from zucchini hypocotyls : the use of chlorotetracycline as a probe for ca uptake. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):47–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Calcium transport and monovalent cation and proton fluxes in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):636–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. J., Silbergeld E. K., Brown R. R., Haynes D. H. Erythrosin B (USFD&C RED 3) inhibits calcium transport and atpase activity of muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1306–1311. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Sigel E., Carafoli E. The purified Ca2+ pump of human erythrocyte membranes catalyzes an electroneutral Ca2+-H+ exchange in reconstituted liposomal systems. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2350–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Calcium transport driven by a proton motive force in vacuolar membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5614–5617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okorokov L. A., Kulakovskaya T. V., Lichko L. P., Polorotova E. V. H+/ion antiport as the principal mechanism of transport systems in the vacuolar membrane of the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 18;192(2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., De Michelis M. I., Pugliarello M. C., Marrè E. H-pumping driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish: stimulation by fusicoccin. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):121–125. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Pugliarello M. C., De Michelis M. I. Electrogenic transport of protons driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish : biochemical characterization. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):200–205. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufogalis B. D., Akyempon C. K., Al-Jobore A., Minocherhomjee A. M. Regulation of the Ca2+ pump of the erythrocyte membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:349–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker K. S., Sze H. A Ca/H Antiport System Driven by the Proton Electrochemical Gradient of a Tonoplast H-ATPase from Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Dec;79(4):1111–1117. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Scarborough G. A. Active transport of calcium in Neurospora plasma membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3102–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


