FIGURE 5.
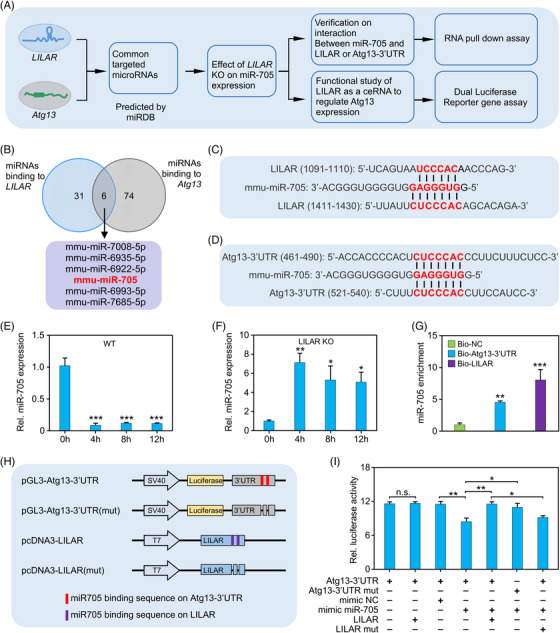
LILAR decreases lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐induced autophagy‐related protein 13 (Atg13) expression in liver cells through competitive binding with miR‐705. (A) An integrated approach to identify the mechanism by which LILAR regulates ATG13 in liver cells. (B) Venn diagram of miRNAs binding to LILAR or the 3′‐untranslated region (UTR) of Atg13 predicted by miRDB. (C and D) The predicted miR‐705 binding sites (red text) on LILAR (C) and the 3′UTR of Atg13 (Atg13‐3′UTR) (D). (E and F) Quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR) quantitation of miR‐705 expression in wild‐type (WT) (E) and knockdown (KO) (F) mice treated without or with LPS for 4, 8, and 12 h. n = 3/group. (G) RNA pulldown assay to validate the interaction of miR‐705 with LILAR or Atg13‐3′UTR. After RNA pulldown with biotinylated probes for LILAR or Atg13‐3′UTR, qRT‐PCR was performed to detect miR‐705 in the pulldown mixture. n = 3/group. (H) Schematic construction of pGL3 vectors carrying WT Atg13‐3′UTR or with miR‐705 binding site deletion and pcDNA3 vectors containing WT LILAR or with miR‐705 binding site deletion. Predicted binding sites of miR‐705 are illustrated in red for Atg13‐3′UTR and in purple for LILAR. (I) Dual‐luciferase reporter gene assay showing LILAR competitive binding with miR‐705 to increase Atg13 expression. n = 3/group. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; n.s., no significance.
