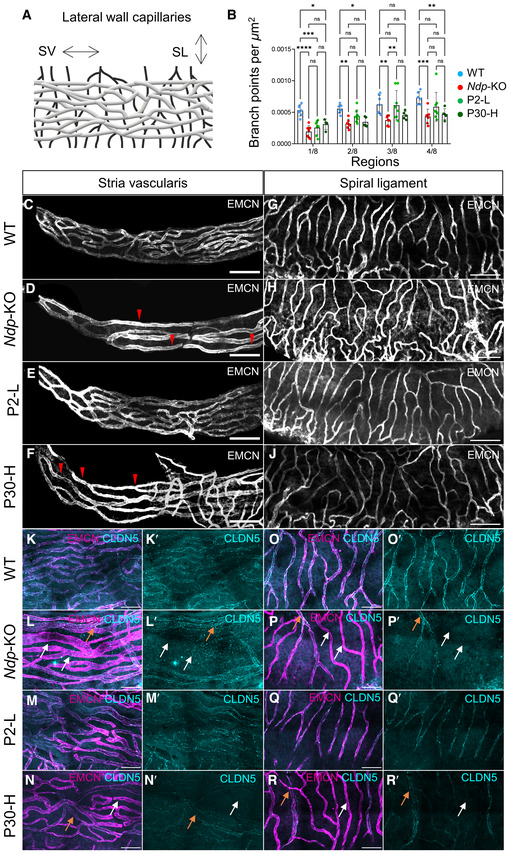
Figure 6. Differences of early and late treatment efficacy for the rescue of the cochlear vasculature at 2 months.
-
ASchematic of the lateral wall vasculature. SL, spiral ligament; SV, stria vascularis capillaries.
-
BQuantification of capillary branching point numbers per area in sequential apical regions 1–4 along the stria vascularis. Branchpoint number was significantly reduced in Ndp‐KO compared to WT. Note that branching was improved more in the P2‐L than in the P30‐H treatment groups. No significant differences in capillary branch point number between WT and Ndp‐KO were detected in the rest of the cochlea, regions 5–8. n = biological replicates. WT, n = 6; Ndp‐KO, n = 6; P2‐L n = 8; P30‐H, n = 5.
-
C–FCapillary network density and morphology at the apical tip of the stria vascularis labelled by anti‐endomucin staining (EMCM). Scale bar: 100 μm, n = 4 per each group. (C) WT, n = 4; (D) Ndp‐KO, n = 4; (E) P2‐L, n = 5; (F) P30‐H, n = 4. Red arrowheads indicate reduced network density and enlargement of vessel diameter.
-
G–JCapillary network density by anti‐endomucin staining (EMCM) in the spiral ligament showing more irregular branching vasculature in Ndp‐KO and P30‐H compared to WT and P2‐L. Scale bar: 100 μm, n = 4 per each group. (G) WT, (H) Ndp‐KO, (I) P2‐L, (J) P30‐H.
-
K–RImmunostaining for tight junction marker claudin‐5 (CLDN5) in anti‐endomucin stained capillaries of the stria vascularis (K–N) and the spiral ligament (O–R). Claudin‐5 shows atypical uneven expression in Ndp‐KO and P30‐H compared to regular labelling of vessels in WT and P2‐L samples. White arrows indicate atypical vessels labelled with endomucin but with low/absent claudin‐5, and orange arrows indicate endomucin‐stained vessels with high claudin‐5 expression. Scale bar 50 μm.
Data information: B data are shown as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis: two‐way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, all values compared to WT (blue) and Ndp‐KO (red). Post hoc test values: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001; ns, non‐significant.
Source data are available online for this figure.
