Figure 4. In silico identification of candidate FBXW7 targets reveals enrichment of Wnt pathway components including LEF1 and TCF7L2.
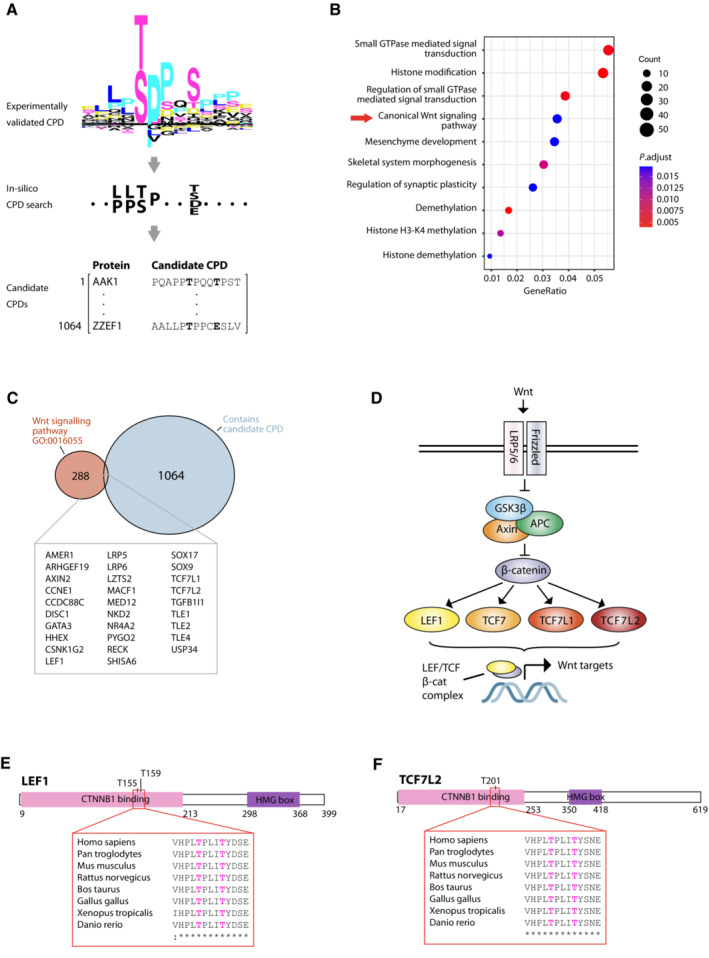
- Schematic indicating workflow for in silico identification of candidate FBXW7 targets carrying putative conserved phosphodegrons (CPDs). Experimentally validated FBXW7 CPDs (top, provided as Dataset EV8) were used to define a consensus motif (middle) for search against the human proteome to identify candidate FBXW7 targets (bottom).
- Dot plot showing enrichment analysis of 1,064 putative FBXW7 substrates against GO biological processes.
- Venn diagram showing overlap between putative FBXW7 substrates identified by in silico analysis and Wnt pathway components curated by the Gene Ontology Consortium (GO:0016055).
- Simplified representation of Wnt signalling pathway. Following stimulation by Wnt ligand, the GSK3β/Axin/APC destruction complex is inhibited and β‐catenin can translocate to the nucleus where it complexes with TCF/LEF family transcription factors to regulate Wnt target gene expression.
- Schematic of putative FBXW7 substrate LEF1 indicating position and conservation of candidate CPD, and phosphorylation sites corresponding to the ‘0’ and ‘+4’ positions curated in PhosphoSitePlus database.
- Corresponding schematic for putative FBXW7 substrate TCF7L2.
Source data are available online for this figure.
