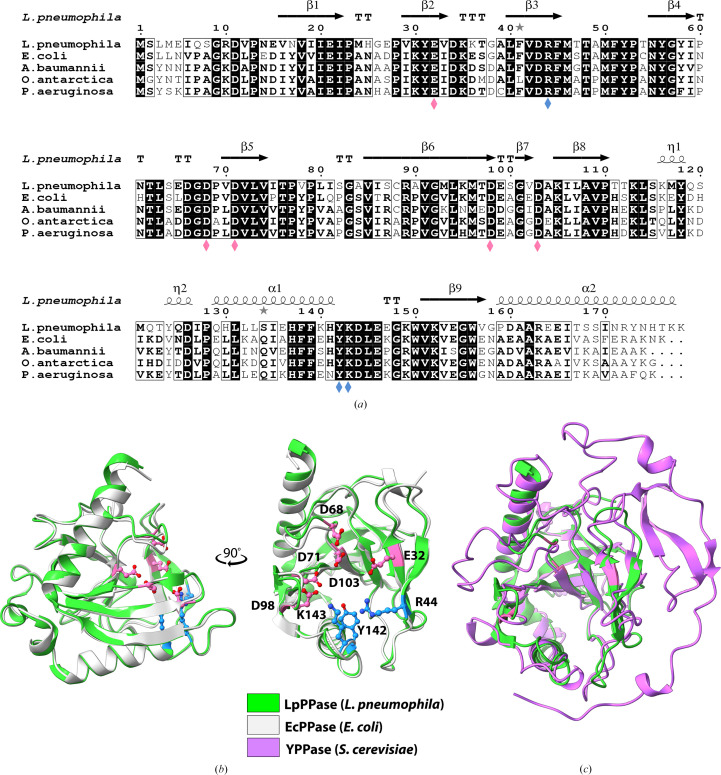
Figure 2.
Sequence and structural alignments of LpPPase. (a) Primary-sequence alignment of L. pneumophila PPase (LpPPase; PDB entry 6n1c) with PPases from A. baumannii (PDB entry 6k21), E. coli (PDB entry 1obw), O. antarctica (PDB entry 3i4q) and P. aeruginosa (PDB entry 4xel). Secondary-structure elements of LpPPase are shown: β-sheets (β), α-helices (α), 310-helices (η), β-turns (TT) and α-turns (TTT). Identical residues are shown in white on a black background, while conserved residues are shown in bold and related residues are boxed. Pink diamonds indicate catalytically significant residues and blue diamonds indicate residues that bind the substrate. (b) LpPPase (green) aligned with EcPPase from E. coli (gray; PDB entry 1obw). Labeled residues shown as sticks are important for catalysis (pink) or for substrate binding (blue), corresponding to the diamonds in (a). (c) LpPPase (green) aligned with YPPase from S. cerevisiae (purple; PDB entry 1e6a), a eukaryotic family I PPase.