Abstract
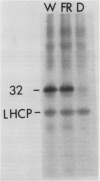
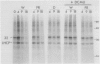
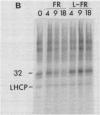
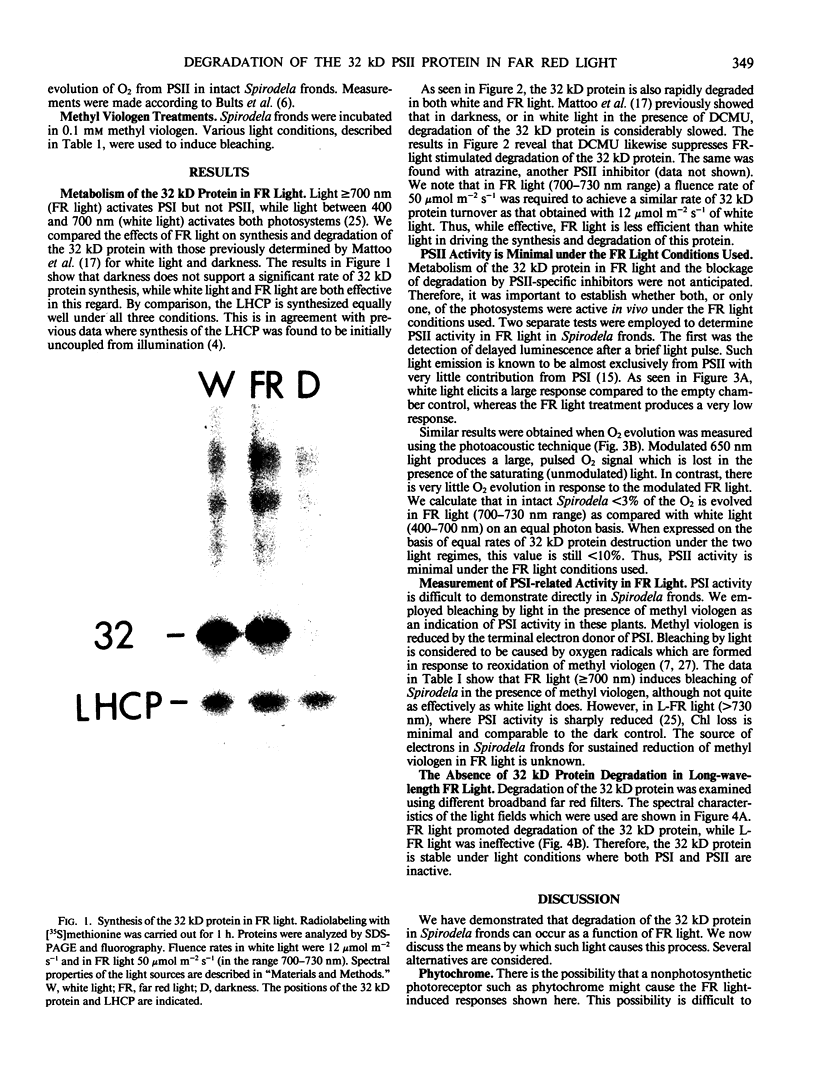
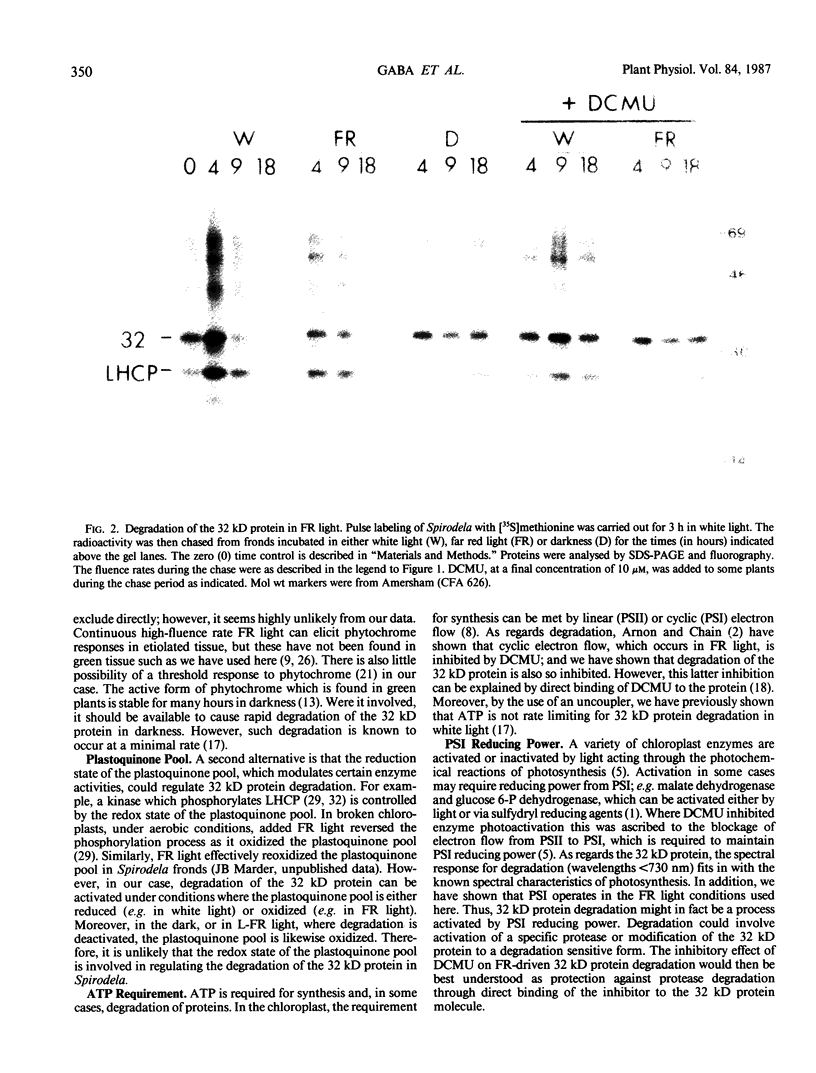
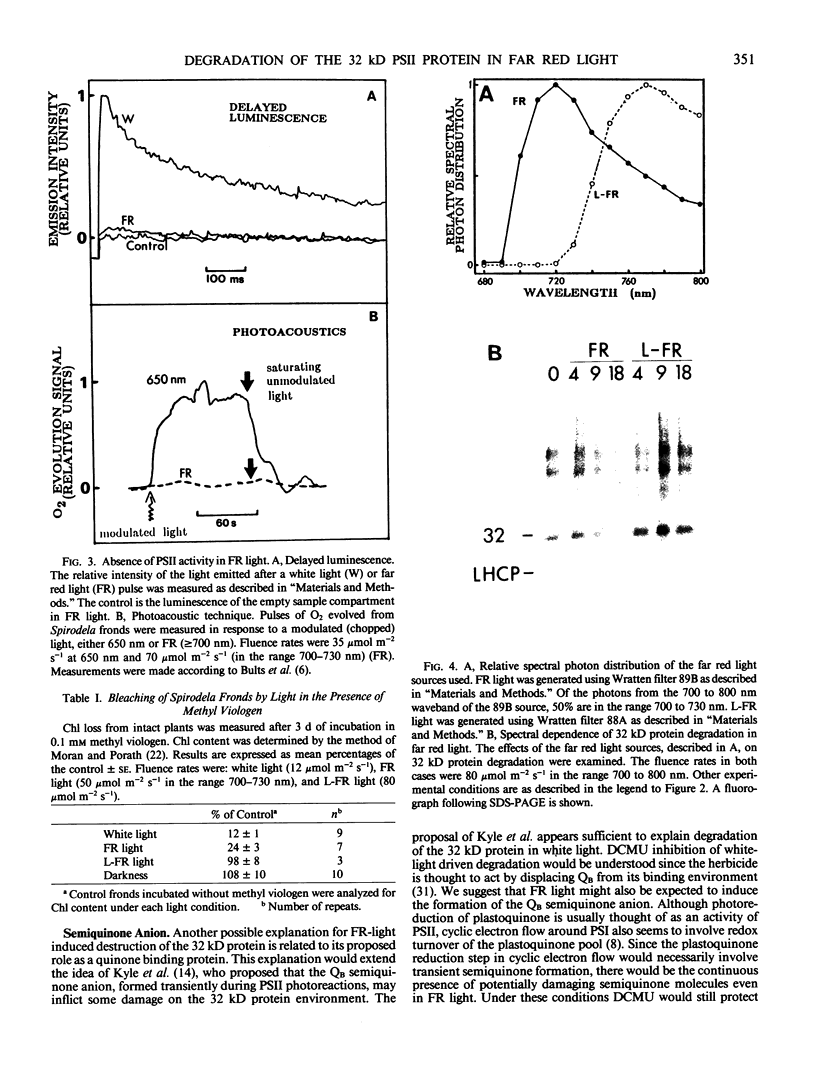
White light (400-700 nanometers) supports the activity of photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II while far red light (≥700 nanometers) supports PSI almost exclusively. In intact fronds of Spirodela oligorrhiza, turnover of the 32 kilodaltons herbicide binding protein is stimulated under both these light conditions, although not in the dark or at wavelengths >730 nanometers. As is the case in white light, the far red light induced degradation of the protein is inhibited by DCMU. The means by which far red light operates is unclear. Hypotheses considered include: PSI activated proteolysis, PSI-induced formation of semiquinone anions, and PSI-generated free radicals.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Nehrlich S. C., Champigny M. L. Light modulation of enzyme activity: activation of the light effect mediators by reduction and modulation of enzyme activity by thiol-disulfide exchange. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):601–605. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I., Chain R. K. Regulation of ferredoxin-catalyzed photosynthetic phosphorylations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4961–4965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Polypeptide turnover in darkness. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):61–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R. L., Packer L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. II. Role of electron transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jun;125(3):850–857. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90523-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. J., Ohad I., Arntzen C. J. Membrane protein damage and repair: Selective loss of a quinone-protein function in chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4070–4074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Hoffman-Falk H., Marder J. B., Edelman M. Regulation of protein metabolism: Coupling of photosynthetic electron transport to in vivo degradation of the rapidly metabolized 32-kilodalton protein of the chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1380–1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Pick U., Hoffman-Falk H., Edelman M. The rapidly metabolized 32,000-dalton polypeptide of the chloroplast is the "proteinaceous shield" regulating photosystem II electron transport and mediating diuron herbicide sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1572–1576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran R., Porath D. Chlorophyll determination in intact tissues using n,n-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):478–479. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollman F. A., Delepelaire P. Correlation between changes in light energy distribution and changes in thylakoid membrane polypeptide phosphorylation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):1–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]