Figure 1.
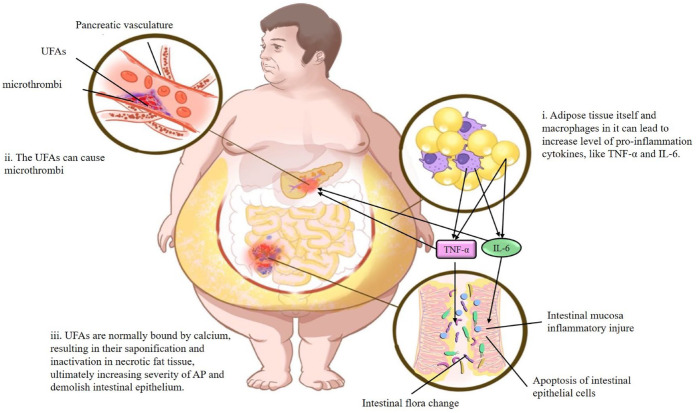
The negative effect of obesity and hypertriglyceridemia both on AP and GM.
(i) The adipose tissue itself and macrophages in it can lead to increase level of pro-inflammation cytokines, like TNF-α and IL-6. These cytokines cause intestinal mucosa inflammatory injury, apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells, and intestinal flora alteration. (ii) In the obesity or hyperlipidemia, the UFAs transmitted from lipolysis of circulating triglycerides can cause microthrombi formation in the pancreatic vasculature resulting in ischemia and pancreatic infarction. (iii) UFAs are normally bound by calcium, resulting in their saponification and inactivation in necrotic fat tissue, ultimately increasing severity of AP and demolish intestinal epithelium.
AP, acute pancreatitis; GM, gut microbiota.