Figure 1.
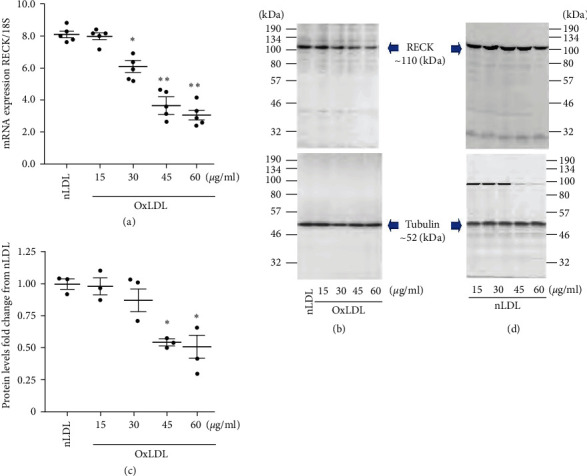
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) suppresses RECK expression in primary human aortic smooth muscle cells (SMC). (a–c) OxLDL, but not nLDL, suppresses RECK mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner. Quiescent SMCs were exposed to OxLDL at indicated concentrations for 2 hr. RECK expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR using a validated TaqMan™ probe (a; n = 5). Native LDL (nLDL, 45 µg/ml) served as a control. 18s served as an invariant control. The mRNA expression was presented as a ratio of RECK mRNA to corresponding 18s rRNA. RECK protein levels were analyzed by Western blotting (b, n = 3). Tubulin served as an invariant control. Intensity of immunoreactive bands from three independent experiments was semiquantified by densitometry, and the ratio of RECK to corresponding Tubulin was presented as fold change from nLDL. (d) nLDL up to 60 mg/ml had no significant effects on basal RECK expression. Quiescent SMC incubated with nLDL up to 60 mg/ml for 2 hr were analyzed by western blotting, and a representative image of three independent experiments is shown. (a) ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus nLDL (n = 5), (b) ∗P < 0.05 versus nLDL (n = 3).
