Figure 3.
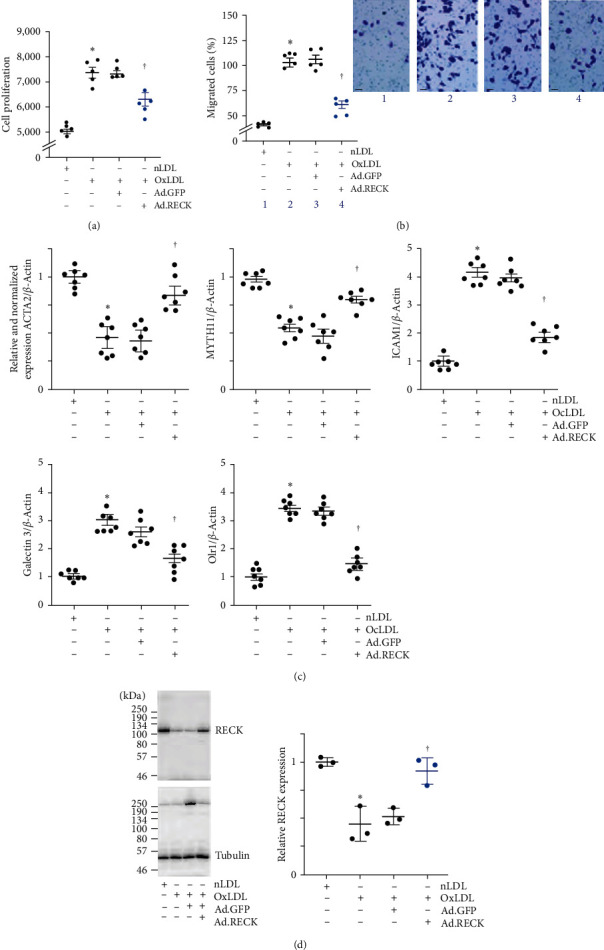
Ectopic expression of RECK blunts OxLDL-induced SMC proliferation and migration. (a, b) Pathophysiological concentrations of OxLDL induce SMC proliferation (a) as analyzed by the CyQUANT GR dye assay and migration (b) analyzed by the Boyden chamber assay. SMCs migrating to the lower surface of the membrane were counted at 20x magnification in 10 independent fields and summarized as mean ± SEM. The inset shows representative images of Matrigel™ transwell invasion. (c) OxLDL induced proinflammatory phenotype changes in SMC. SMC transduced with Ad.RECK or Ad.GFP (moi10 for 24 hr) were exposed to OxLDL (45 mg/ml for 48 hr) and analyzed for SMC markers αSMA and MYH11, and proinflammatory markers ICAM1, Galectin 3, and Olr1. (d) OxLDL does not inhibit ectopically expressed RECK. SMCs transduced with Ad.RECK were made quiescent, exposed to OxLDL for 48 hr, and analyzed for RECK expression by western blotting. (a) ∗P < 0.01 versus nLDL, †P < 0.05 versus Ad.RECK (n = 5), (b) ∗P < 0.01 versus nLDL, †P < 0.05 versus. Ad.RECK (n = 5), (c) ∗P < 0.01 versus nLDL, †P < 0.05 versus OxLDL ± Ad.GFP, (n = 5), (d) ∗P < 0.05 versus nLDL, †P < 0.05 versus OxLDL or OxLDL + Ad.GFP (n = 3).
