Figure 8.
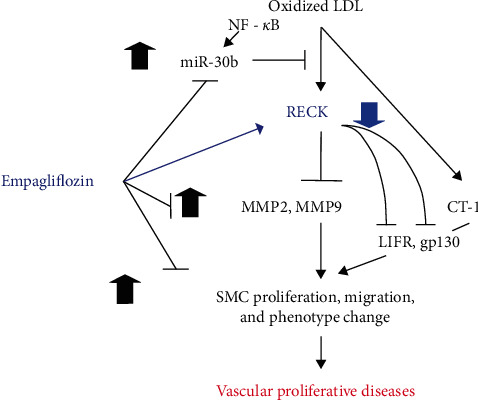
Schematic showing that pretreatment with empagliflozin inhibits OxLDL and CT-1-induced SMC proliferation, migration, and proinflammary phenotype changes. Exposure to OxLDL-induced NF-κB-dependent miR-30b expression and miR-30b-mediated RECK suppression. Pretreatment with empagliflozin reversed these effects. Further, OxLDL induced MMP2 and MMP9 activation, and forced expression of RECK or pretreatment with empagliflozin blunted this response. OxLDL induced CT-1 expression and CT-1-stimulated SMC proliferation and migration in part via LIFR and gp130. Ectopic expression of RECK inhibited these effects by potentially associating with LIFR and gp130. Importantly, empagliflozin blunted CT-1-induced mitogenic and migratory effects. These results suggest the therapeutic potential of RECK overexpression or empagliflozin in vascular proliferative diseases.
