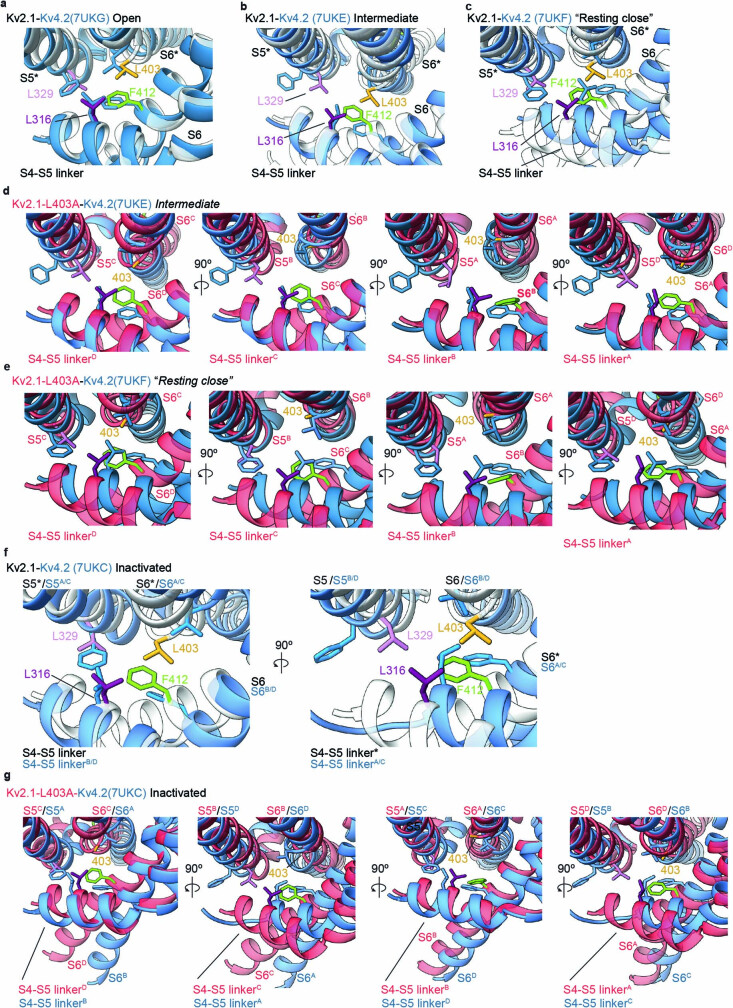
Extended Data Fig. 9. Structural alignment of Kv2.1 and Kv4.2 channels proposed to be in open, intermediate, resting/close or inactivated states.
a) Close-up view of the hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in Kv2.1 (white) and an open state of Kv4.2 (blue). b) Hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in Kv2.1 (white) and an intermediate state of Kv4.2 (blue). c) Hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in Kv2.1 (white) and a resting/close state of Kv4.2 (blue). d) Hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in the four protomers of the L403A mutant of Kv2.1 (red) and an intermediate state of Kv4.2 (blue). e) Hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in the four protomers of the L403A mutant of Kv2.1 (red) and a resting/close state of Kv4.2 (blue). f) Close-up view of the hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in Kv2.1 (white) and the two distinct protomers present in an inactivated state of Kv4.2 (blue). g) Hydrophobic coupling nexus residues in the four protomers of the L403A mutant of Kv2.1 (red) and the two distinct protomers present in an inactivated state of Kv4.2 (blue).