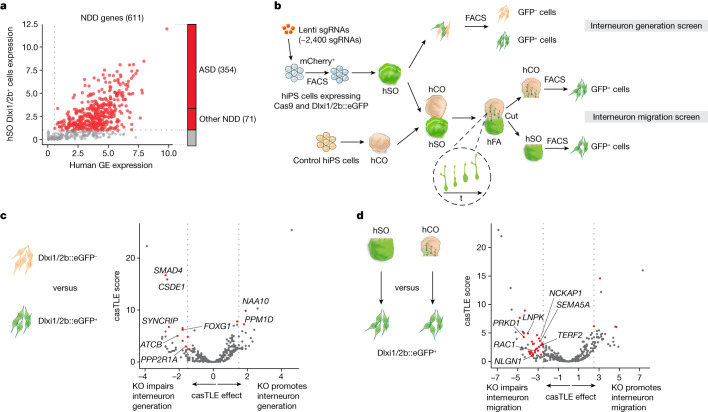
Fig. 1. CRISPR screens of NDD genes reveal regulators of human interneuron generation and migration.
a, A total of 425 genes (labelled in red) out of 611 NDD genes showing expression in hSO Dlxi1/2b::eGFP+ cells and human postconception weeks 8–9 ganglionic eminences were included in the CRISPR screens. Among these, 354 genes are associated with ASD and 71 genes are associated with other NDDs. b, Schematic describing the interneuron generation and migration CRISPR screens. The inset highlights how hSO-derived interneurons migrate into the hCO side of the hFA. hSO were derived from the 1205-4 hiPS cell line and hCO were derived from the 2242-1 hiPS cell line. c, Volcano plot of the casTLE-estimated maximum gene perturbation effect size and associated casTLE score for the interneuron generation screen. Genes with at least two sgRNAs having effects equal to or less than −1.57 or equal to or more than +1.57, roughly twice the standard deviation (s.d.) of negative controls, were selected as candidates (red), with labels for cell cycle genes and genes that were subsequently validated. d, Volcano plot of the casTLE-estimated maximum gene perturbation effect size and associated casTLE score for the interneuron migration screen. Genes with at least two sgRNAs having effects equal to or less than −2.5 or equal to or more than +2.5, roughly twice the s.d. of negative controls were selected as candidates (red), with labels for cytoskeleton and cell migration genes and genes that were subsequently validated.