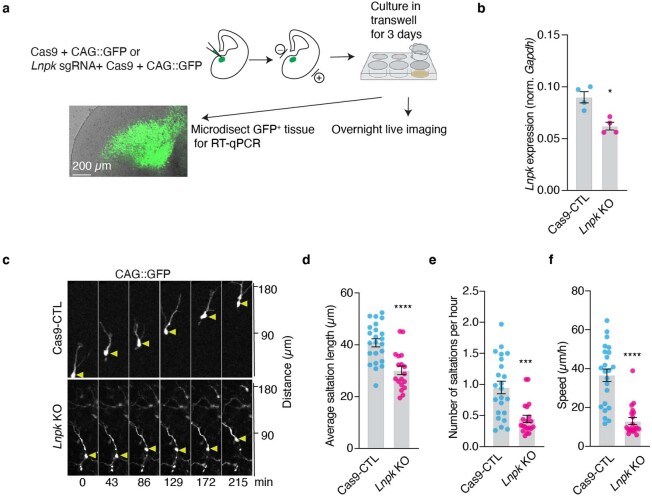
Extended Data Fig. 6. Loss of Lnpk affects mouse interneuron migration.
a, Schematic illustrating the experimental design for investigating the role of LNPK in mouse interneuron migration. b, Quantification of Lnpk mRNA expression in the microdissected tissue (n = 4, each datapoint represents microdissected slices from 2-3 embryos). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m.; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. * P = 0.0286. c, Representative time-lapse sequences of live cell imaging showing the saltatory migration of GFP+ cells in slices electroporated with pCAG-IRES-GFP and CAS9 protein or pre-mixed sgRNAs-Cas9 complex targeting mouse Lnpk. Triangles mark the nucleus. d–f, Quantification of the saltation length (d, two-tailed unpaired t-test; **** P < 0.0001), number of saltations (e, two-tailed Mann-Whitney test; *** P = 0.0002), and speed of movement of electroporated cells (f, two-tailed Mann-Whitney test; **** P < 0.0001). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m.; Cas9-CTL, n = 23 cells; Lnpk KO, n = 20 cells; from 10 embryos).