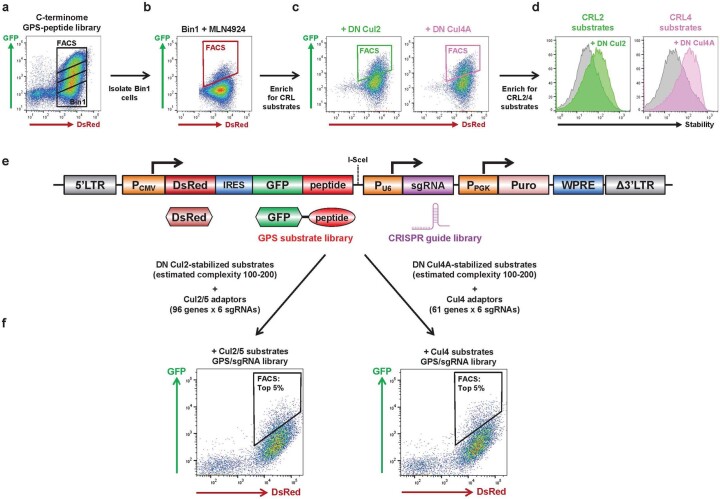
Extended Data Fig. 1. Generation of multiplex CRISPR screen libraries to interrogate C-terminal degrons targeted by Cullin-RING E3 ligases.
a-d Derivation of cells expressing C-terminal peptides targeted by Cul2 complex or Cul4 complexes. Starting from HEK-293T cells expressing the C-terminome GPS-peptide library12, we isolated the most unstable GFP-peptide fusions (Bin1) (a), treated them with MLN4924, and then isolated cells in which the GFP-peptides fusions were stabilized (b). After recovery in the absence of MLN4924, to further purify substrates of specific Cullin complexes we expressed dominant-negative (DN) versions of either Cul2 (green) or Cul4A (pink) and again isolated the cells in which the GFP-peptides fusions were stabilized by FACS (c). After recovery, we re-challenged the sorted cells with the DN Cullins to verify that the final populations of cells were highly enriched for CRL substrates (d). e,f, Generation of the multiplex CRISPR screening vector to examine C-terminal degrons targeted by Cullins. e, Schematic representation of the multiplex CRISPR screening vector. GFP-fusion peptides were amplified from the genomic DNA of the cells in (d) by PCR and cloned into the lentiviral vector downstream of GFP; the CRISPR sgRNA library targeting either Cul2 or Cul4 adaptors was then cloned into the resulting substrate library using the I-SceI site to generate the dual GPS-sgRNA multiplex CRISPR screening library. f, The library was then introduced into HEK-293T stably expressing Cas9, and the top ~5% of cells expressing the most stable substrates were isolated by FACS. Genomic DNA was then extracted from both the sorted cells and the unsorted libraries, and substrate-sgRNA pairs enriched in the sorted cells quantified by paired-end Illumina sequencing.