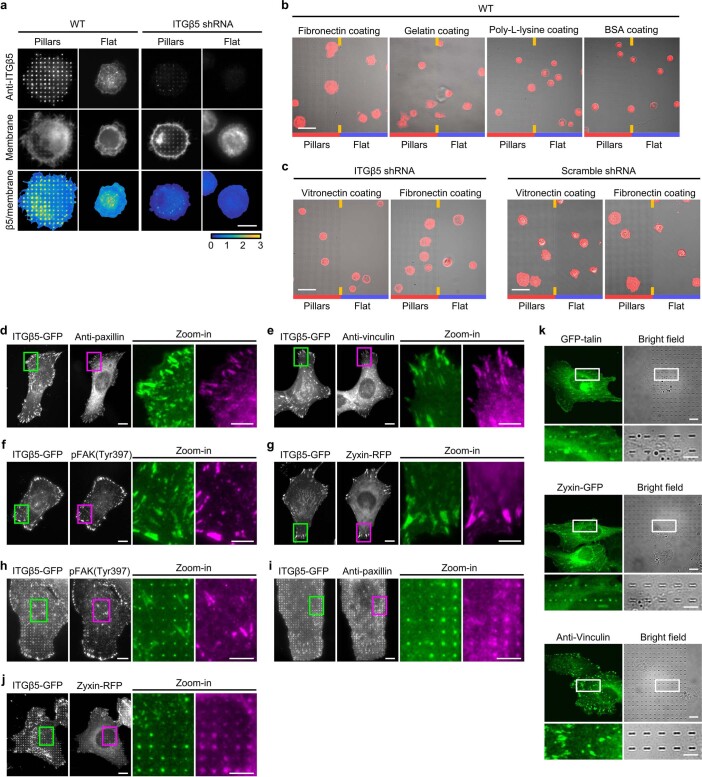
Extended Data Fig. 4. Curved adhesions promote early-stage cell spreading and involve a subset of focal adhesion proteins.
a, ITGβ5 accumulates at vitronectin-coated nanopillars within 30 min after seeding. Cells spread to a larger area on nanopillars compared to on flat areas on the same substrate. Knockdown of ITGβ5 with shRNAs largely abolished the nanopillar-induced early cell spreading. Scale: 10 µm. b, Overlay of bright-field and fluorescence images of wild type (WT) U2OS cells stably expressing GFP-CaaX on both nanopillars and flat surfaces in the same imaging fields. The cells were seeded on substrates and cultured for 30 min before imaging. Scale: 50 µm. c, Overlay of bright-field and fluorescence images of U2OS cells transduced with ITGβ5 or scramble shRNAs and stably expressing GFP-CaaX on both nanopillar arrays and flat surfaces in the same imaging fields. The cells were seeded on substrates and cultured for 30 min before imaging. Scale: 50 µm. d to g, Fluorescence images showing that ITGβ5-GFP colocalizes with focal adhesion proteins paxillin (d), vinculin (e), pFAK (Tyr397) (f), and zyxin (g) at focal adhesion-like patches in U2OS cells on vitronectin-coated flat surfaces. Scale: full-size, 10 µm; insets, 5 µm. h to j, Representative fluorescence images showing that ITGβ5-GFP accumulation at vitronectin-coated nanopillars spatially correlates with paxillin (i) and zyxin (j), but not with pFAK (Tyr397) (h) in U2OS cells. The cell membrane was marked with transiently expressed surface SNAP-tag conjugated with AF647. The normalized ITGβ5/membrane was used to measure ITGβ5 accumulation for the correlation quantification in Fig. 3b. Scale: full-size, 10 µm; insets, 5 µm. Endogenous paxillin, vinculin, and pFAK (Tyr397) were immunolabelled. Zyxin was tagged with RFP and transiently expressed (d-j). k, Fluorescence images of cells cultured on nanobars showing that GFP-talin and zyxin-GFP preferentially accumulate at the nanobar ends. However, anti-vinculin shows no accumulation at nanobar locations. Scale: full-size, 10 µm; insets, 5 µm.