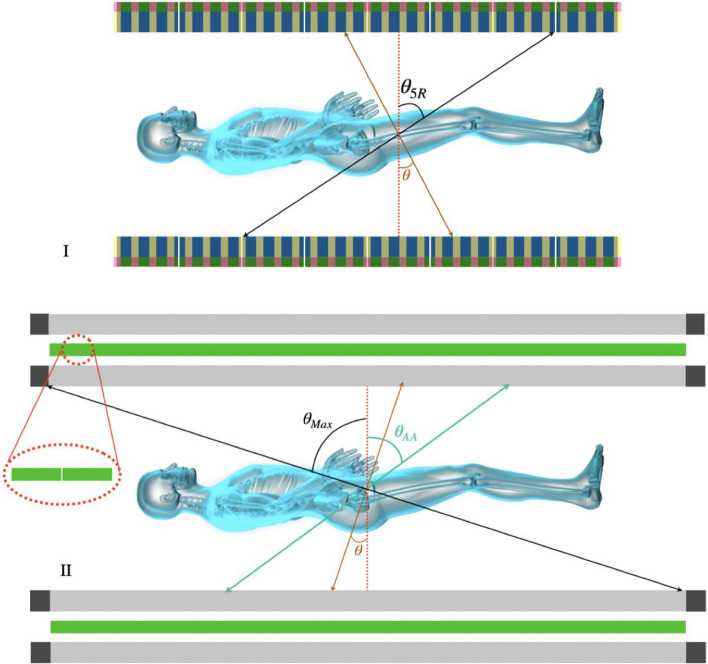
Fig. 3.
Schematic visualization of uEXPLORER (I) (blue) [8, 10, 13]) and sparse geometry (transparent yellow) with 194.8 cm of AFOV and dual layers. TB J-PET (II) with axially arranged plastic scintillators (gray) coupled with SiPMs (black) at each end and arrays of WLS (green) between each layer. The oblique LORs (with large values of ) have a negative contribution in the spatial resolutions due to the parallax error. To avoid it, uEXPLORER uses a ring-based cut that accepts the coincidences within a maximum of 5 rings. As shown in figure (II), TB J-PET uses continuous plastic scintillators (gray), denotes the acceptance angle applied for it to cut oblique LORs. demonstrate the largest angle of detectable oblique coincidences