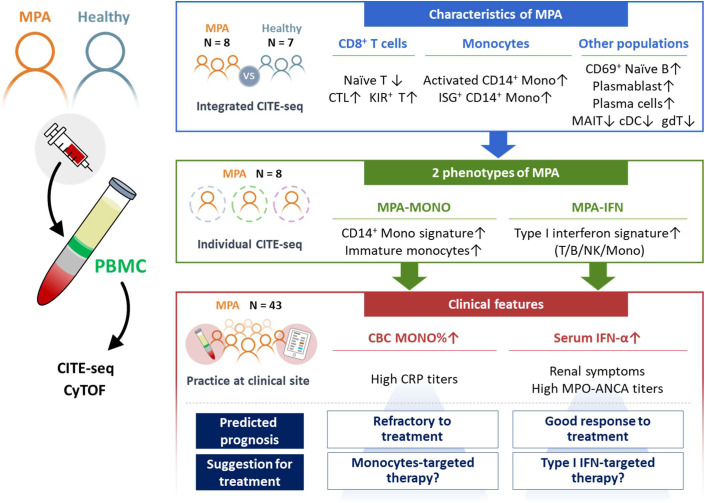
Fig. 6. Graphical scheme of this study.
Newly-onset, untreated patients with MPA (n = 8) and healthy donors (n = 7) were recruited for this study. MPA is characterized by increased proportions of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, KIR+ CD8+ T cells, activated CD14+ monocytes, CD14+ monocytes with ISG expression, CD69+ naïve B cells, plasmablasts, and plasma cells. MPA was further subclassified into two groups based on the high expression of CD14+ monocytes signature genes (MPA-MONO) or high expression of ISGs (MPA-IFN). The percentage of monocytes and serum IFN-α levels were the clinical markers that clearly distinguished MPA-MONO and MPA-IFN groups, respectively. The findings of this study suggest clinical recommendations for estimating prognosis for each patient based on the immunological phenotypes of MPA. MPA microscopic polyangiitis, PBMC peripheral blood mononuclear cells, CITE-seq cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes by sequencing, CyTOF cytometry by time-of-flight, CTL cytotoxic T lymphocytes, KIR killer immunoglobulin-like receptor, ISG interferon signature genes, MAIT mucosal associated invariant T cells, cDC classical dendritic cells, gdT gamma-delta T cells, CBC complete blood count.