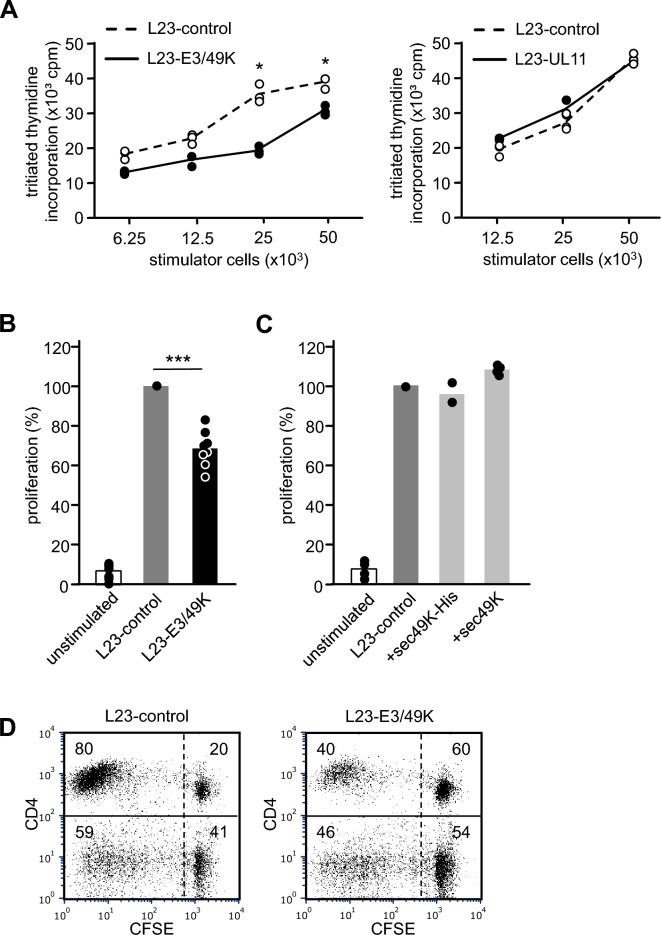
Figure 2.
Influence of viral E3/49K and pUL11 on human PBMC proliferation. (A) Assessment of PBMC proliferation by tritiated thymidine incorporation. Human PBMC (1 × 105/well) were stimulated with increasing numbers of irradiated L23-control, L23-E3/49K or L23-UL11 cells. The cells were cultured for 5 days, pulsed with tritiated thymidine and harvested after 16 h. One representative experiment out of a series of eight and four is shown comparing the stimulatory capacity of L23-E3/49K and L23-UL11 cells, respectively, with L23-control cells. Results are expressed as mean cpm of triplicate cultures. Statistical analysis was performed by applying the paired Student’s t-test. (B) Proliferative responses of PBMC from eight different human blood donors to stimulation with L23-control and L23-E3/49K cells. 1 × 105 human PBMC were stimulated with 25 × 103 irradiated L23 cells. Proliferation was determined after 6 days. Results are expressed as percent proliferation relative to L23-control cells (100%). Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA. (C) Studies using soluble E3/49K. Human PBMC (1 × 105/well) were stimulated with irradiated L23-control cells (25 × 103/well). Culture was performed without soluble E3/49K (unstimulated) or in the presence of purified soluble E3/49K (sec49K-His; n = 2) or supernatant from L23-E3/49K cells (sec49K; n = 4). The cells were cultured for 5 days, pulsed with tritiated thymidine and harvested after 16 h. Results are expressed as percent proliferation relative to cultures without E3/49K (100%). (D) Assessment of T cell proliferation by CFSE dilution. Human PBMC (1 × 105/well) were stained with CFSE and stimulated with irradiated L23-control or L23-E3/49K cells (25 × 103/well). The cells were cultured for 7 days, stained with anti-CD4-mAb and analyzed by flow cytometry. The numbers represent % positive cells in each quadrant of the representative histograms.