Figure 1. Lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) Levels, Concordance in High Lp(a) Levels, and Numbers Needed to Screen Among Relatives of Index Participants With High Lp(a) Levels.
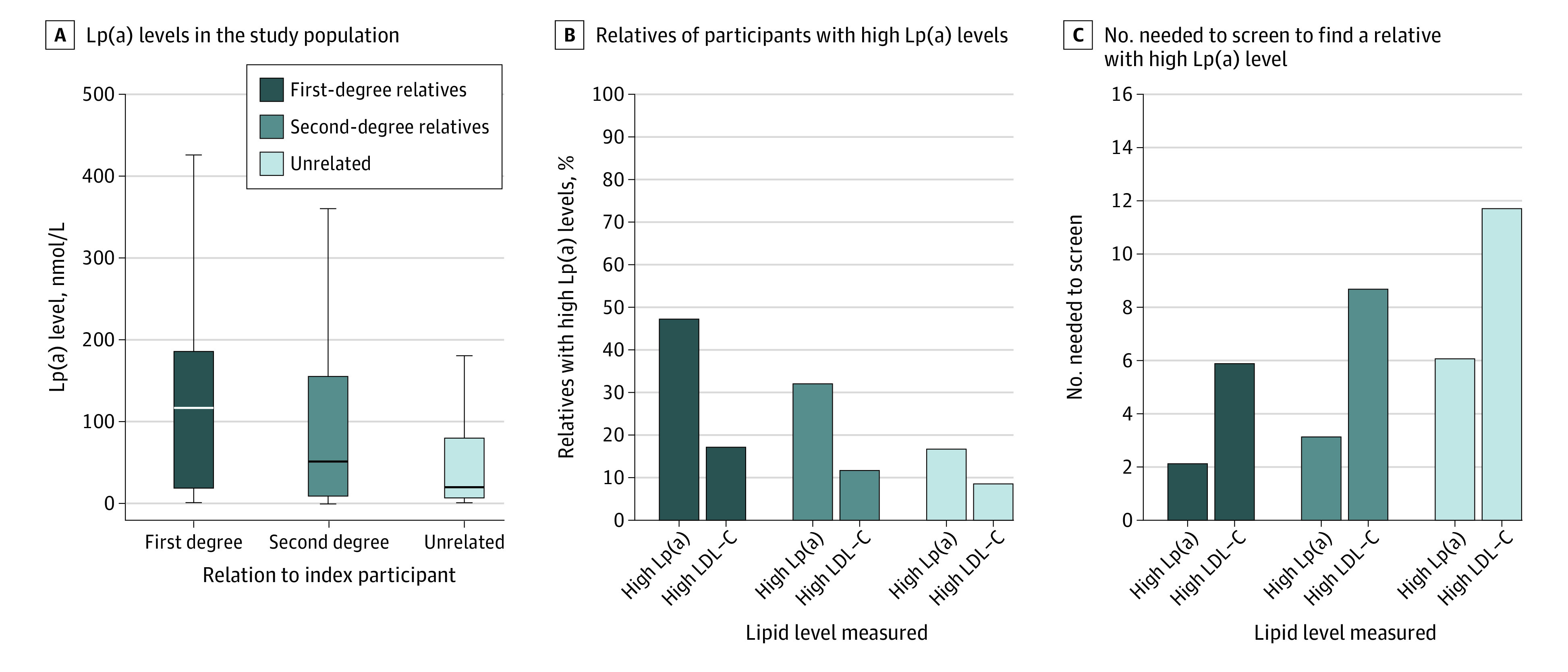
Concentrations of Lp(a) in relatives of index participants with high Lp(a) levels (≥125 nmol/L [to approximate levels in mg/dL, divide by 2.15]) for first- and second-degree relatives (A) resulted in a high percentage of relatives who also have high Lp(a) levels (B) and a low number needed to screen to identify 1 relative with high Lp(a) levels (C). As a comparator, Lp(a) concentrations in unrelated randomly matched pairs of individuals with high Lp(a) are included in all panels, and the concordance and number needed to screen among relatives is also shown for high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (≥190 mg/dL [to convert to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0529]). In panel A, vertical lines indicate medians, boxes indicate IQRs, and error bars indicate the largest and smallest data point, but not further than 1.5 times the IQR.
