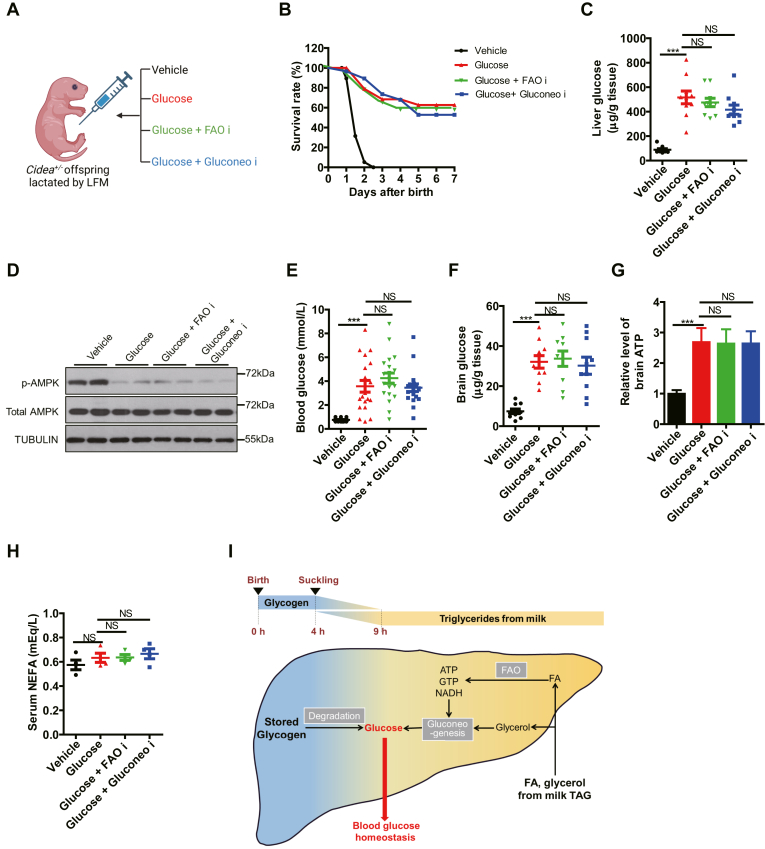
Fig. 6.
Glucose is a universal energy source for neonates. A: Schematic of the rescue experiments with glucose. From 6 h after birth, the pups lactated by Cidea−/− females (low-fat milk, LFM) were injected with four solutions every 8 h: vehicle, Glucose, Glucose + FAO i and Glucose + Gluconeo i, respectively. B: The survival rate of different groups in (A) (n = 15). C: Hepatic levels of glucose (n = 10). D: Protein expression in livers by Western blotting (n = 2). E: Blood glucose level (n = 20). F, G: Brain glucose (F) and ATP (G) level (n = 10). H: The level of serum NEFA (n = 4). I: Model depicting the role of glycogen and milk TAG in maintaining neonatal blood glucose homeostasis. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Data were analyzed using a two-tailed Student’s t test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. FAO, fatty acid oxidation; NEFA, nonesterified fatty acid; TAG, triacylglyceride.