Fig. 1.
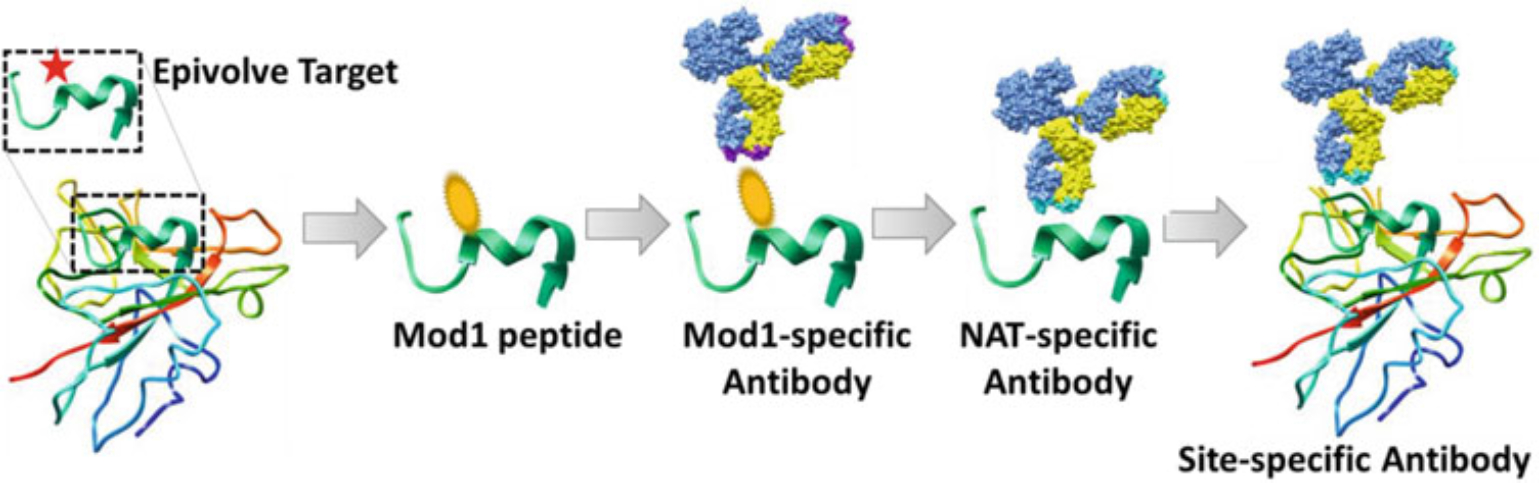
Illustration the principles of Epivolve technology. An important residue (the Epivolve targeted site) on the target protein is chosen. A 10–15-mer peptide of the target sequence will then be synthesized with the modification on the Epivolve targeted amino acid, named mod1-peptide. This mod1-peptide is biopanned using a naïve phage display library to generate a mod1-specific Ab. The identified mod1-specific Abs are then mutagenized using error-prone PCR to generate a Discovery Maturation (DisMat) library. The DisMat library is then biopanned against the NAT peptide (or full-length protein if available) to identify anti-NAT (or anti-full-length protein) clonotypes. The resulting anti-NAT Abs can be further engineered for increased binding affinities using Affinity Maturation (AffMat)
