Fig. 2.
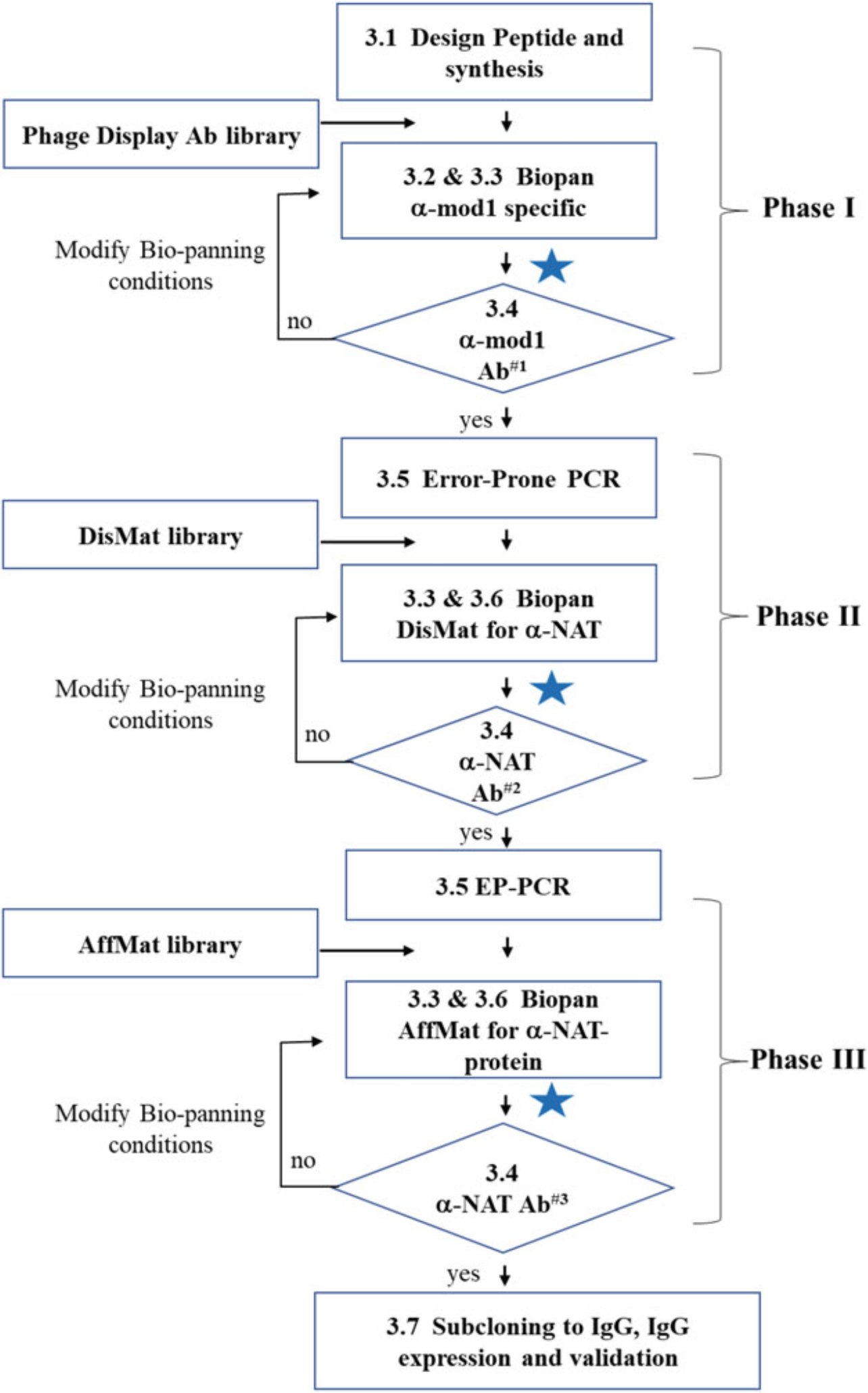
In vitro Epivolve workflow Developing site-specific Abs using Epivolve technology by in vitro phage display can be illuminated as 2 phases (Discovery and DisMat) and an optional third phase (AffMat). In Phase I, discovery biopanning against a mod1-peptide is used to identify mod1-specific scFvs. In phase II (DisMat), anti-mod1 specific scFvs from phase I are used as the template for Error-Prone PCR to make DisMat libraries. The DisMat library is then biopanned against a NAT peptide or full-length protein to identify anti-NAT clones. In the optional Phase III (AffMat), anti-NAT clones are subjected to a second round of Error-Prone PCR to make AffMat libraries. These libraries are then used to develop high-affinity and high-specificity anti-NAT peptide or an-NAT full-length protein Abs, which will be validated by the appropriate applications such as by MILKSHAKE Western-blot [25], ELISA, and other functional assays. The blue star indicates where there are several steps in between the two steps shown, which can include phage supernatant ELISA, scFv protein expression and purification with details we have published [2, 19]. Typical result of Ab#1 is shown in Fig. 3a. Typical results of Ab#2 and Ab#3 are shown in Fig. 3b and Fig. 3c
