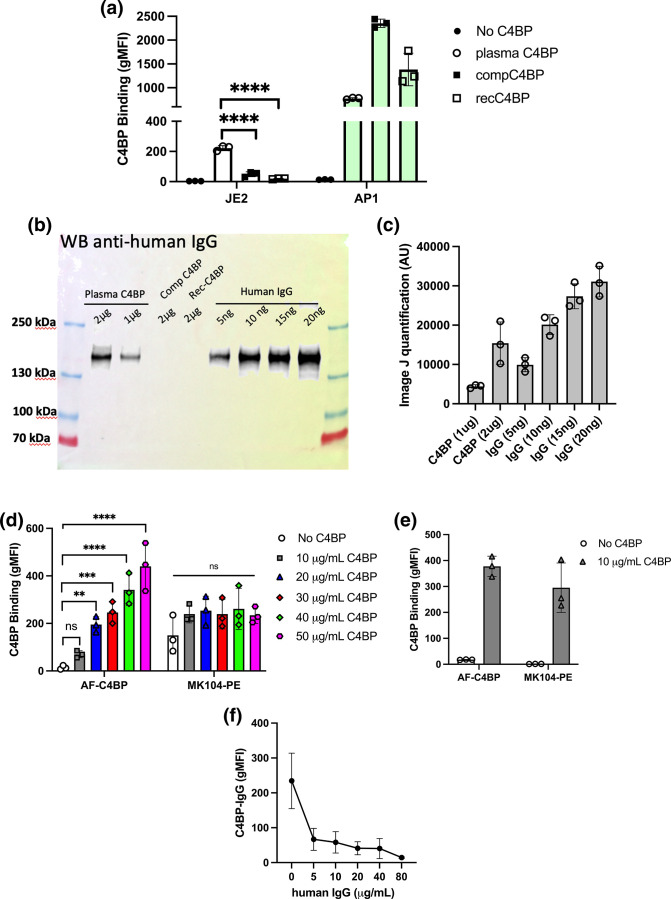
Fig. 4.
Plasma purified C4BP interaction with S. aureus occurred via IgG co-purified with C4BP. (a) Dy488-labelled plasma purified C4BP (plasma C4BP), commercially obtained C4BP (compC4BP) and recombinantly produced C4BP (recC4BP) were incubated with S. aureus strain JE2 or S. pyogenes strain AP1. Binding was analysed by measuring the geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) using a BD FACS Canto flow cytometer. (b) Plasma C4BP (1 and 2 µg), compC4BP (2 µg) and recC4BP (2 µg) were probed for human IgG contamination using goat anti-human IgG-HRP. Purified human IgG at concentrations between 5–20 ng was used as a control C) Image J quantification of western blot analysis (n=3; Fig. S2). (d) Dy488-labelled plasma C4BP was incubated with S. aureus strain JE2 at concentrations between 0–50 µg ml−1. Fluorescence was either measured at 488 or following incubation of bacteria with F(ab’)2 MK104 mouse anti-C4BP antibodies and secondary goat anti-mouse – PE antibodies. (e) Dy488-labelled plasma C4BP (10 µg ml−1) was incubated with S. pyogenes strain AP1 and binding analysed as described in (d). (f) S. aureus strain JE2 was pre-incubated with increasing concentrations of human IgG. Dy488-labelled plasma purified C4BP (10 µg ml−1) binding was analysed by measuring the gMFI using a BD FACS Canto flow cytometer. Bars indicate the mean; data points represent three biological replicates and error bars inform the standard deviation. (a–d) Statistical differences were calculated using a one-way ANOVA analysis using Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 ****P<0.0001,.