FIG 2.
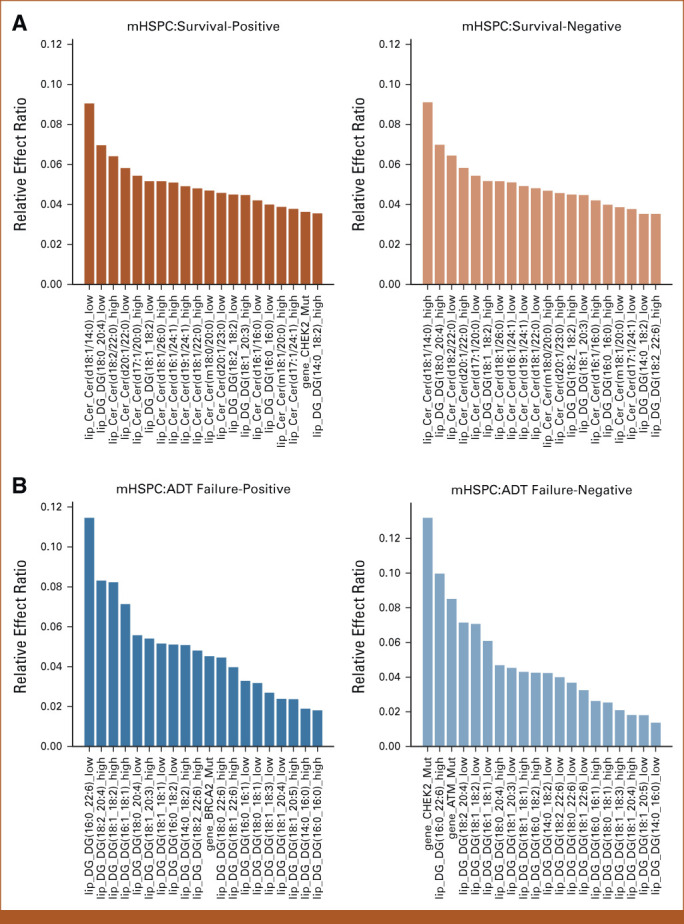
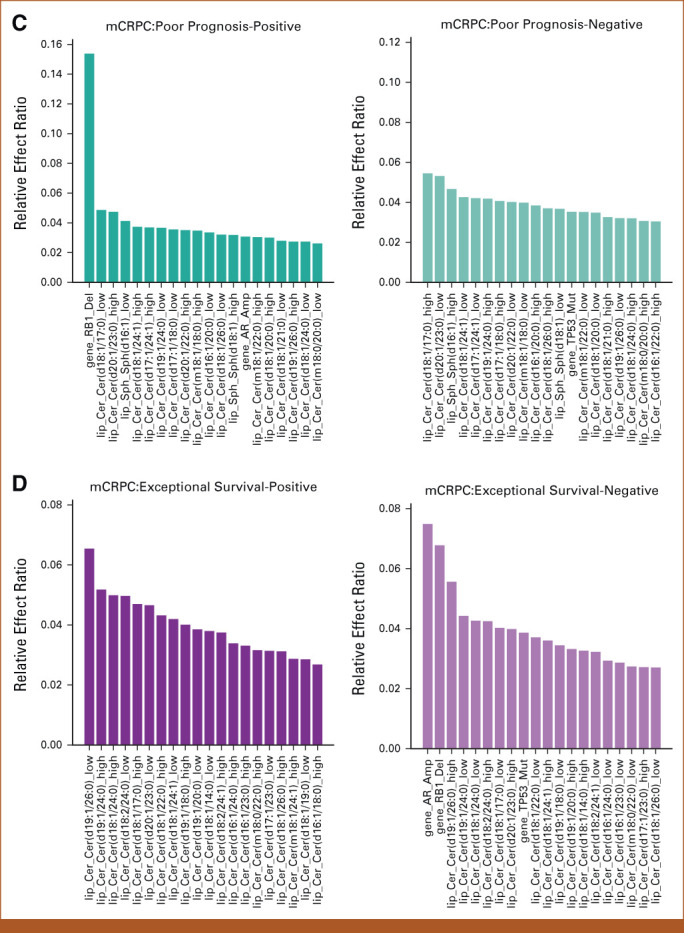
Results of feature effects analysis for association of multi-omic classifier with clinical outcomes. (A-D) For each target task, the top 20 genomic and lipidomic features with most positive and negative effects along with their relative effect ratios are shown respectively. Machine learning was used to compute feature weights. The relative effect ratio computations are in the Data Supplement ([Supplementary Methods]). (A) Top 20 multi-omic features with most positive and negative effects associated with survival prediction in mHSPC state. (B) Top 20 multi-omic features with most positive and negative effects on ADT-failure prediction in mHSPC state. (C) Top 20 multi-omics features with most positive and negative effects associated with poor prognosis prediction in mCRPC state. (D) Top 20 multi-omics features with most positive and negative effects on exceptional survival prediction in mCRPC state. Acy, acylcarnitine; ADT, androgen-deprivation therapy; Cer, ceramide; DG, diacylglycerol; Gene, genomic feature sets; mCRPC, metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer; mHSPC, metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer; Sph, sphingolipid; TG, triacylglycerol.
