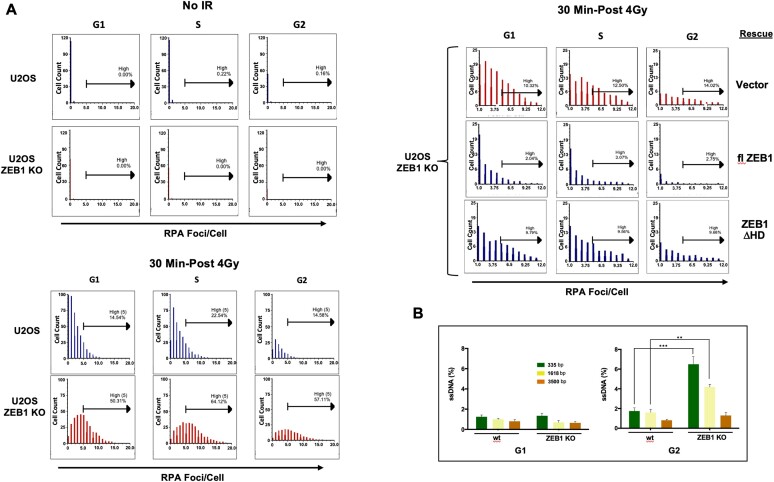
Figure 6.
ZEB1 Inhibits resection. (A) Imaging FLOW cytometry shows that, in response to IR, ZEB1 inhibits number and intensity of RPA2-labled foci. Top left panel, in either wt or ZEB1 KO U2OS cells, in the absence of IR, there are virtually no detectable RPA2-positive foci; Bottom left panel, blue bars, 30 min after 4 Gy, wt cells with RPA2-positive foci appear in all three CC phases, with cells in S having the highest percentage of cells with greater than 5 foci per cell (high spot count); their ZEB1 KO counterparts, depicted with red bars, show a significant increase in high spot count in all three phases. Upper right panel, ZEB1 KO cells stably expressing the indicated constructs were subjected to 4 Gy and processed for Imaging FLOW cytometry as above; compared to vector control (red bars, top row), expression of flZEB1 cDNA dramatically reduces RPA2-positive foci, while the homeodomain deletion (ΔHD) mutant has a minimal effect (bottom row). A minimum of 20000 cells were analyzed per condition. Data shown in this panel are representative of three independently performed analyses (carried out on separate days). (B) ZEB1 inhibits resection at an enzymatically-induced DSB. An AsiSI-generated DSB was induced in synchronized DIvA cells (see Supplementary Figure S7A for WB of these ZEB1 KO U2OS cells), genomic DNA isolated, digested with restriction enzyme BsrGI and subjected to qPCR (in triplicate) using PCR primers that flank BsrGI sites at 335, 1618 or 3500 bp downstream of an AsiSI cut site on chromosome I. Resection, yielding increased levels of SS DNA and subsequent PCR product, is increased in asynchronized cells with ZEB1 KD, a result amplified in G2. Results, normalized to AsiSI cutting efficiency (see Supplementary Table S1 and Materials and Methods), are the avg. of three different expts. with S.E.M. * P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.005.