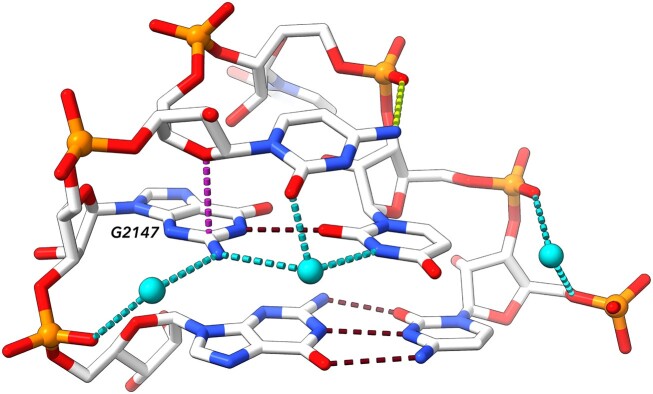
Figure 1.
Examples of interactions in an RNA molecule. Some of the most important interactions are highlighted in dashed lines: base pairing hydrogen bonds in dark red, sugar-base stacking in dark violet, phosphate-base hydrogen bond in yellow, water-formed hydrogen bonds in cyan (waters are depicted as cyan balls). The bottom pair is canonical Watson–Crick, the pair above is a G–U pair ‘locked’ by interaction with bridging water molecule. G2147 is in syn orientation and dinucleotide C2146–G2147 is in the left-handed Z-form conformation (note the inverted direction of the ribose of C2146 further stabilized by stacking its O4’ to the guanine aromatic ring). Displayed is a six nucleotide loop from 80 nucleotide long fragment of 23S RNA from Thermus thermophilus complexed with ribosomal protein L1 (PDB ID: 4qvi) (5).