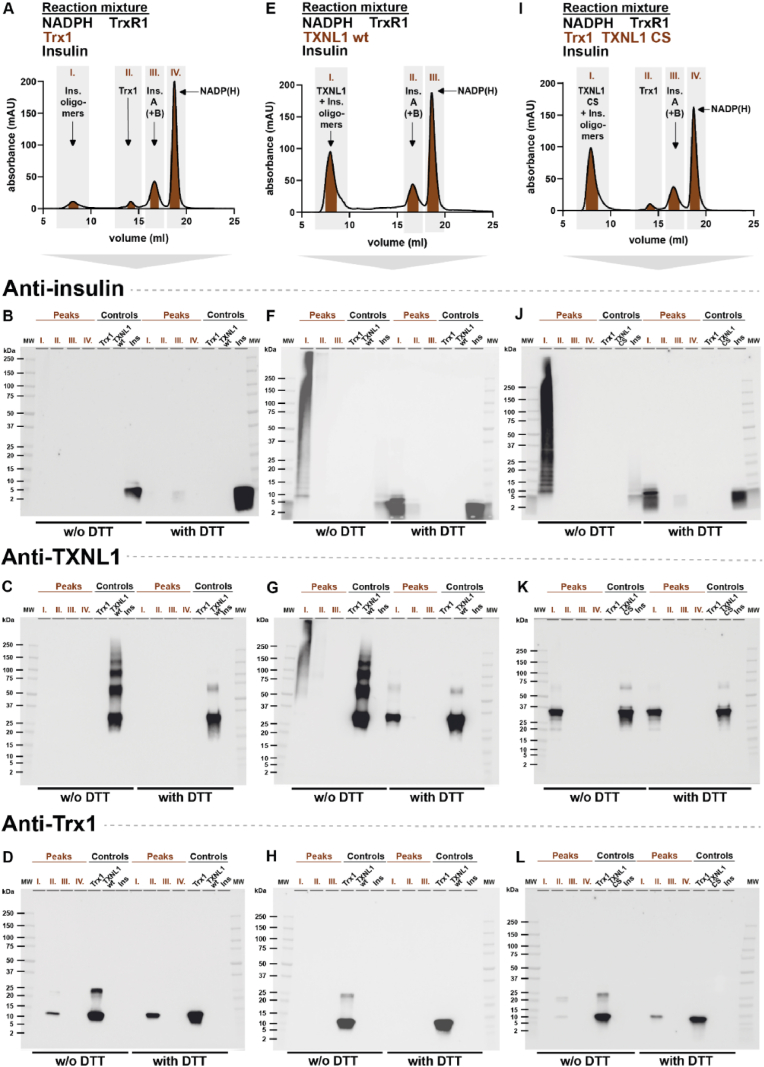
Fig. 7.
TXNL1 but not Trx1 makes high-molecular weight complexes with reduced insulin. Insulin reduction assays were performed in higher volumes and subsequently evaluated by gel filtration and with key fractions further analyzed for the presence of specific protein components using Western blots. All chromatography runs were performed as with the pure components shown in Fig. 6. Here the chromatograms after reactions with (A) solely Trx1-catalyzed insulin reduction, (E) addition of TXNL1 to the Trx1-catalyzed reaction, and (I) addition of cysteine-less TXNL1 CS to the Trx1-catalyzed reaction are shown, with identification of Peaks I, II, III and IV as indicated, elution volumes at the x-axes and absorbance at 280 nm at the y-axes. Fractions of each peak were also analyzed by Western blot analyses, blotting fractions from (A), (E) and (I) for the presence of (B), (F), (J), insulin, (C), (G), (K), TXNL1 and (D), (H), (L), Trx1, respectively, including controls with pure proteins and analyzing the fractions as well as proteins under non-reducing conditions without (“w/o”) or reducing conditions with DTT, as indicated in the figure panels. All chromatography fractions were loaded in the lanes with the same volume (2 μl each). Controls for the Western blots used were pure insulin (0.33 μg), TXNL1 (0.165 μg) and Trx1 (0.165 μg), added to their respective control lanes, as indicated.