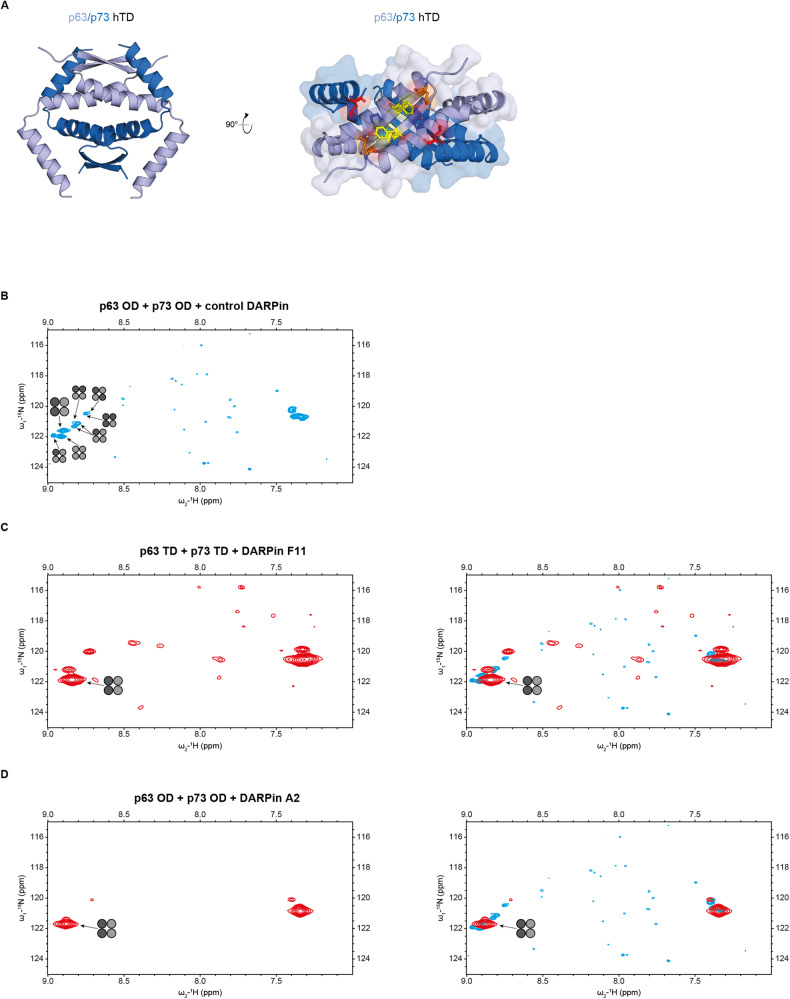
Fig. 1. DARPins bind conformation-selective to the p63/p73 hetero-tetramer.
Structure of the hetero-tetramer assembled by the tetramerization domains of p63 and p73. A The hetero-tetramer of p63/p73 (PDB 2NB1) is composed of two chains of each protein. For clarity reasons, the flexible C-termini of the p63 chains C-terminally of Q409 have been omitted. p63 chains (light blue) and p73 chains (dark blue) each form an independent dimer consisting of an N-terminal antiparallel β-sheet and one subsequent helix per monomer. These helices interact with the corresponding helices from the other dimer, thus forming the central tetramerization interface. Additionally, the C-terminal second helices reach across the tetramerization interface. The C-terminus of the second helix of p73 interacts with the β-sheet of p63, leading to the enhanced stability. The right image shows a view of the p63 β-sheet as a surface model with the second helices of p73 shown as explicit secondary structure element. The hydrophobic outward facing amino acids of the p63 chains are depicted as colored sticks (L361 in orange, Y363 in yellow, P365 in blue). The side chain of L396 of p73 (red, shown as sticks) penetrates into a hydrophobic pocket formed mainly by P365 and L361 of p63. B NMR spectrum of the selectively 15N-Lys labeled p632/p732 hetero-tetramer in the presence of the non-binding control DARPin. Only p73 was labeled, resulting in signals for the two lysine resonances K370 and K372. The signal of K372 in the [15N, 1H]-TROSY spectrum splits after mixing with the unlabeled p63 OD into eight individual signals that correspond to all stoichiometric and conformational possibilities for mixed p63/p73 tetramers. The individual species are marked with tetramer symbols in which light gray symbolizes p63 and dark gray p73. The signal of the p632/p732 hetero-tetramer is labeled with a larger symbol. C Addition of DARPin F11 reduces the complexity with only the p632/p732 hetero-tetramer being strongly populated. A few small peaks representing additional species with a population of less than 20% are visible. The weak resonances spread across the spectrum represent natural abundance peaks of the DARPin. On the right, an overlay of the spectrum on the left and the spectrum shown in (B) is provided. The larger line width of the DARPin - p632/p732 hetero-tetramer complex is due to the larger molecular weight of this complex. D The same as in (C) but with DARPin A2. This DARPin shows an even higher selectivity for the p632/p732 hetero-tetramer with additional resonances representing less than 10% of the population.