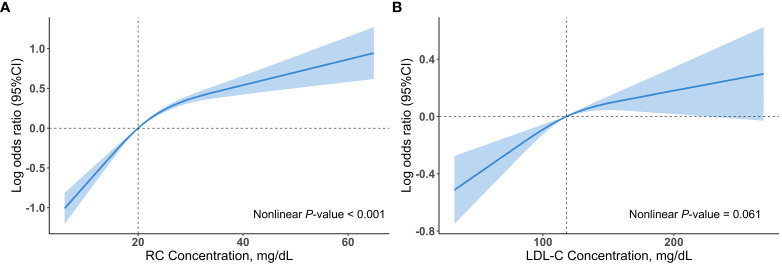
Figure 2.
Associations (log odds ratios, 95%CIs) of RC and LDL-C concentrations with hypertension using a restricted cubic spline regression model in the NHANES 1999 to 2018. (A) Association between RC concentrations and hypertension. (B) Association between LDL-C concentrations and hypertension. Results were adjusted for age (continuous), sex (male/female), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, Mexican American, other), educational level (less than high school, high school or equivalent, college or above), family income-poverty ratio (≤1.0, 1.1-3.0, >3.0), smoking status (never smoker, former smoker, current smoker), alcohol drinking (non-drinker, low to moderate drinker, heavy drinker), chronic kidney disease (yes or no), diabetes mellitus (yes or no), coronary heart disease (yes or no), eGFR (continuous), FBG (continuous), and HbA1c (continuous). All estimates accounted for complex survey design. Restricted cubic spline regression model was conducted with 3 knots. Shadows represent the 95% CIs for the spline model (with respective medians as reference). CI, confidence interval; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; RC, remnant cholesterol.