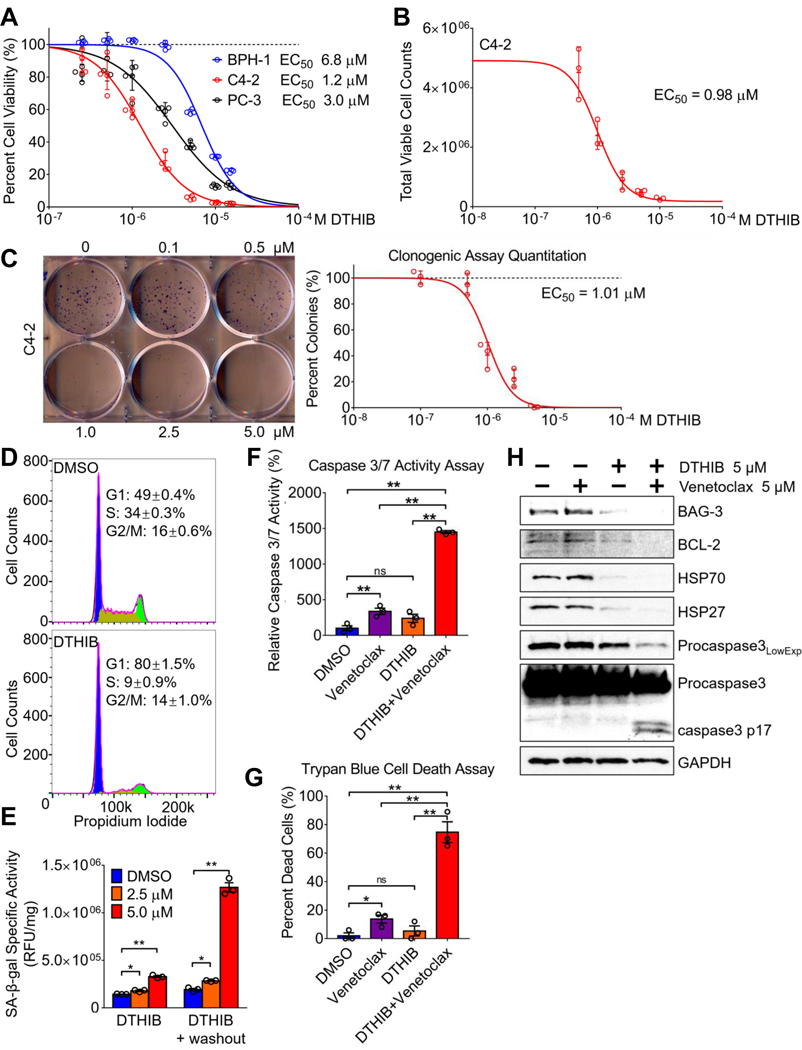
Fig. 5.
DTHIB inhibits human prostate cancer cell proliferation (A) AlamarBlue assays from 96-hour DTHIB treatment preferentially reduced the viability of the malignant prostate cancer cell lines C4–2 and PC-3, as compared to the benign prostate cell line BPH-1 (n = 5). Shown is the calculated EC50 for DTHIB in each cell line (B) Validation of DTHIB efficacy in the C4–2 PCa cell model using the trypan-blue exclusion assay (n = 3). Shown is the EC50 for DTHIB in C4–2 cells calculated with this assay (C) Clonogenic assay of C4–2 cells treated with the indicated concentrations of DTHIB for 10 days. A representative image of C4–2 colonies is shown. Shown is the EC50 for DTHIB in C4–2 cells calculated with the clonogenic assay (D) FACS analysis showing 48-hour 5 μM DTHIB treatment of C4–2 cells induced cell cycle arrest with accumulation in the G1 phase. (E) DTHIB treatment drives C4–2 cells into senescence, indicated by the induction in SA-β-galactosidase activity (n = 3). (F) C4–2 cells were treated with 5μM venetoclax, 5μM DTHIB, or 5μM of venetoclax and DTHIB for 48 hours. Apoptosis in each sample was quantitated by measuring caspase 3/7 enzymatic activity (n = 3). (G) C4–2 cells were treated as described in (F) and the percent dead cells was quantitated using the trypan-blue exclusion assay. (H) Immunoblotting was used to detect changes in key molecular markers involved in the synergy between DTHIB and venetoclax. C4–2 cells were treated the same as described in section (F).