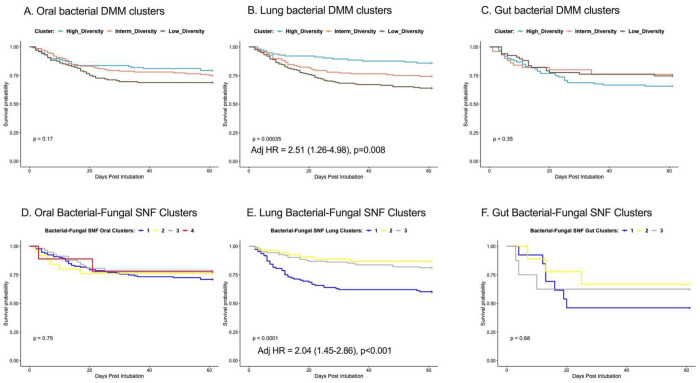
Figure 4: Lung bacterial and bacterial-fungal clusters strongly predicted 60-day survival independent of clinical predictors, organ dysfunction severity and host-response subphenotypes.
A-C: Kaplan-Meier curves for 60-day survival from intubation stratified by oral (A), lung (B) and gut (C) bacterial DMM clusters. The Low-Diversity lung DMM cluster was independently predictive of worse survival (adjusted Hazard Ratio = 2.51 (1.26-4.98), p=0.008), following adjustment for age, sex, history of COPD, immunosuppression, severity of illness by sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores and host-response subphenotypes. The Lung bacterial-fungal SNF cluster with high pathogen and C. albicans abundance (cluster 1) was independently predictive of worse survival (D), whereas the oral and gut bacterial-fungal SNF clusters (D, F) did not impact survival.