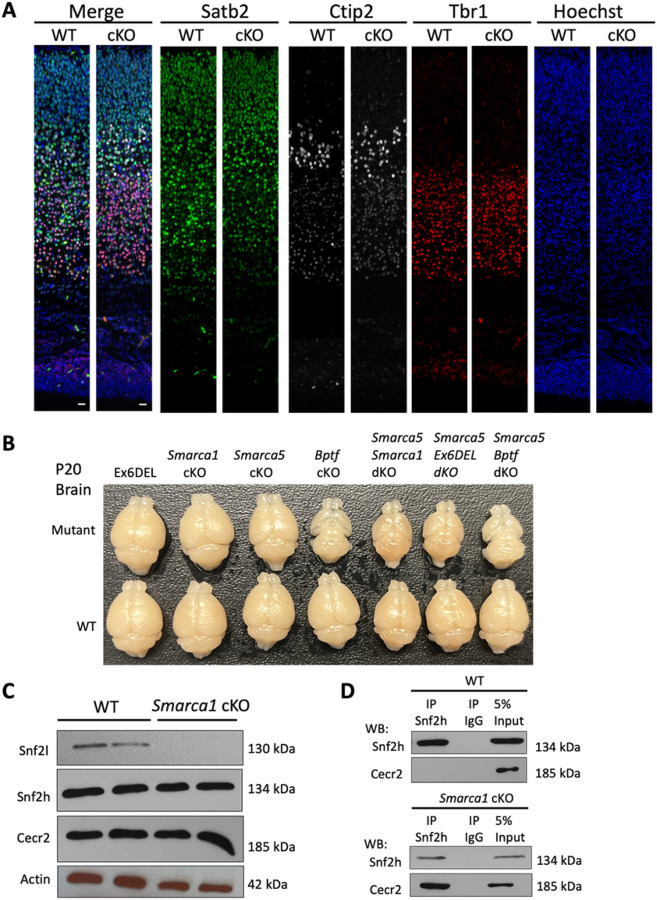
Figure 6: Variations in cortical growth caused by ablation of different NURF components.
A) Control (WT) and Smarca1 cKO (cKO) coronal brain sections isolated at P0 and imaged at the dorsomedial region of the cerebral cortex. Sections were IF-stained for the deep layer neuronal markers Tbr1 (red; layer VI) and Ctip2 (white; layer V), and the upper layer neuronal marker Satb2 (green, layers II-V). The merged images are shown in the left panels. Cell nuclei were counter-stained with Hoechst dye (blue; right panels). Scale bars = 20 mm. B) Photographs of P20 brains dissected from transgenic mice corresponding to the genetic ablation of different genes that comprise the NURF complex (mutant) or from their control littermates (WT). Ex6DEL refers to mice with a deletion of exon 6 of the Smarca1 gene that generates an internally truncated Snf2l protein lacking part of the ATPase/helicase domain. cKO, conditional knockout; dKO, double conditional knockout. C) The CERF complex, comprising Snf2l and Cecr2, is abundantly expressed in the cerebellum. P10 cerebellar extracts were isolated from control (WT) or Smarca1 cKO animals and used for immunoblots to examine CERF protein levels and Snf2h abundance. D) Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed from WT (upper panels) or Smarca1cKO (lower panels) cerebellar extracts with antibodies to Snf2h or rabbit IgG. Snf2h antibodies immunoprecipitated Cecr2 only when Snf2l protein was absent (Smarca1cKO). 5% of the total IP lysate was loaded as input.