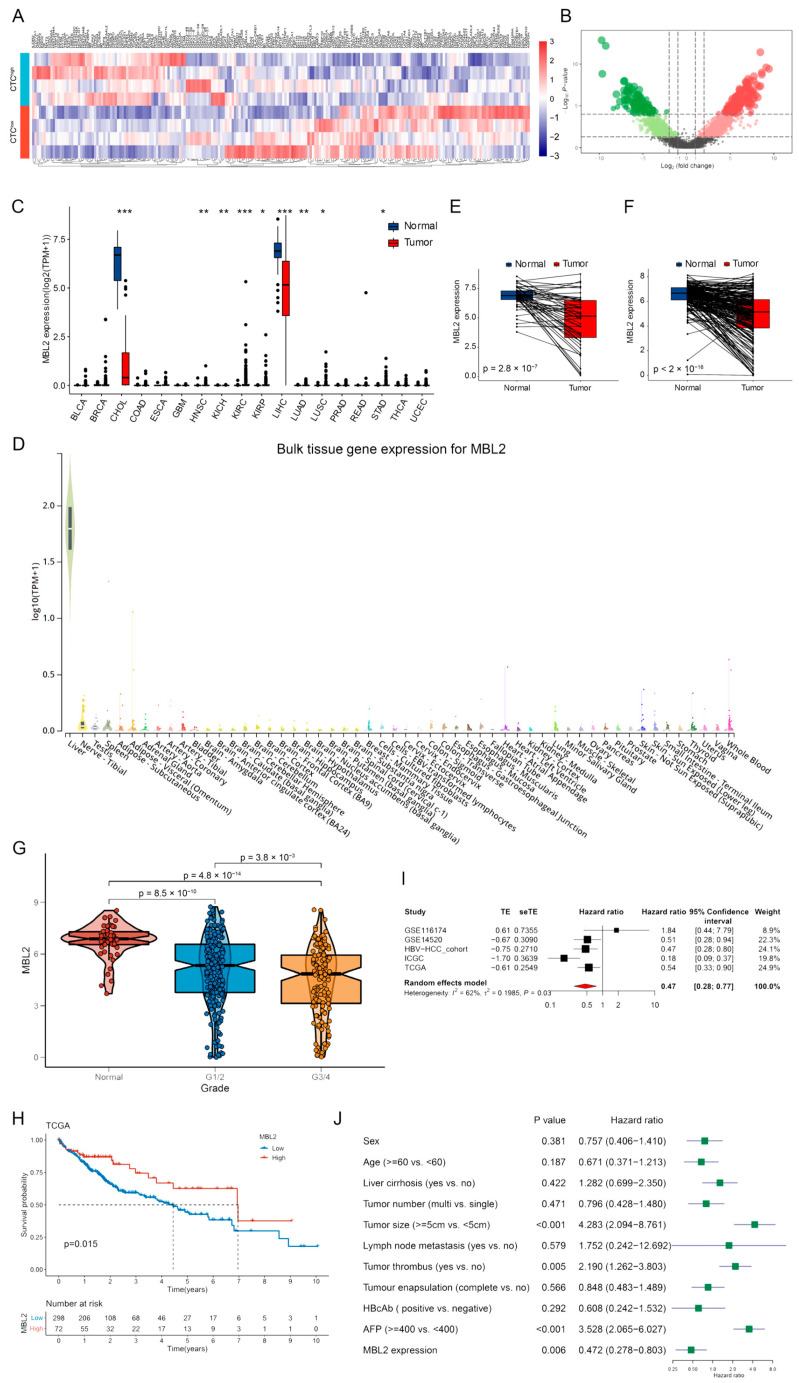
Figure 1.
MBL2 gene expression and prognostic significance. (A) High-throughput sequencing was employed to compare transcriptional expression profiles between the two groups (CTC-high, CTC > 5; CTC-low, CTC = 0). (B) A heat map showing differential gene expression from high-throughput sequencing. (C) TCGA pan-cancer cohorts were used to explore MBL2 gene expression. (D) The GTEx database was utilized to confirm the basal expression of MBL2 in the liver tissue. (E,F) The mRNA expression of MBL2 in tumors and paired adjacent liver tissues from the TCGA and ICGC databases was analyzed. (G) The expression of MBL2 was assessed in normal liver tissue and HCC samples of different tumor grades. (H) Survival analysis of HCC patients based on the expression of MBL2 in the TCGA database. (I) The meta-analysis of the prognostic value of MBL2 expression in five HCC datasets is shown using a forest plot. (J) Univariate Cox regression analyses of MBL2 with other clinical parameters in the HBV-HCC cohort (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). MBL2, mannose-binding lectin 2; CTC, circulating tumor cell; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; GTEx, The Genotype-Tissue Expression Project; ICGC, International Cancer Genome Consortium; HBV-HCC, hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.