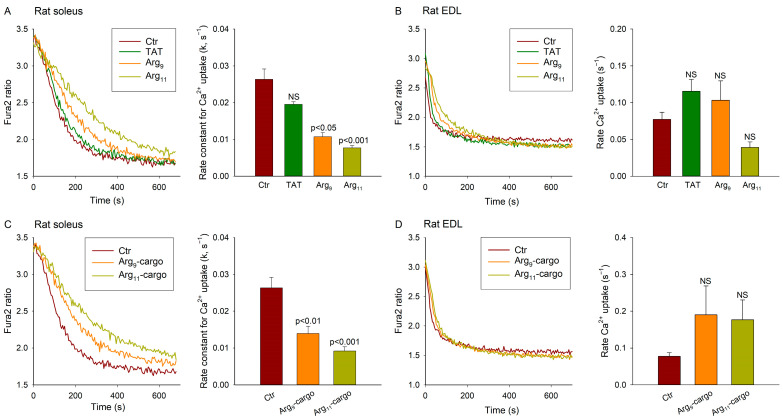
Figure 4.
Effect of CPPs on Ca2+ homeostasis in skeletal muscle. Oxalate-supported Ca2+ uptake was examined in homogenates isolated from the rat soleus and EDL muscles. Comparison was made between untreated homogenates (Ctr) and homogenates incubated with TAT, Arg9, or Arg11. Arg-containing CPPs significantly inhibited Ca2+ uptake in soleus, both in the absence (A) or presence (C) of attached, scrambled cargo. Peptide incubation did not significantly alter Ca2+ uptake in EDL homogenates (B,D). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc correction. p values are indicated versus Ctr. NS = not statistically significant. Nruns in Ctr, TAT, Arg9, Arg11 = 6, 5, 6, 6; nruns in Ctr, Arg9-cargo, Arg11-cargo = 6, 4, 4 in homogenates from 4 soleus muscles; 7, 5, 6, 5 and 7, 4, 4 in homogenates from 4 EDL muscles.