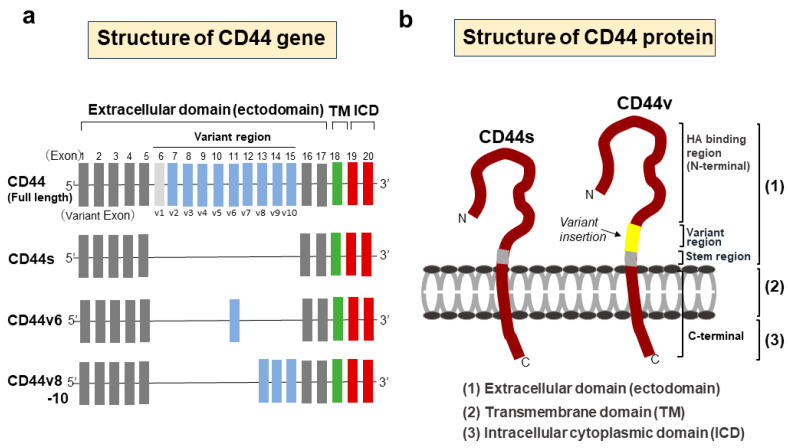
Figure 1.
Structures of CD44 gene and protein. (a) Schematic structures of the CD44 gene. The CD44 gene encodes 20 exons, with exons 6–15 alternatively spliced and inserted into the stem region of CD44 as variant exons. The first five (1–5) and last five (16–20) exons are constant and encode the CD44 standard (CD44s) isoform. Splice variants with variant exons are designated CD44 variant (CD44v) isoforms. The structure of CD44v6 is shown as a representative variant isoform. In humans, v1 exon is lacking due to an in-frame termination codon. (b) Structural domains of the CD44 protein. CD44 consists of three domain regions, including an extracellular domain (ectodomain), transmembrane domain, and cytoplasmic domain. In CD44v, a variant region containing splice variants is inserted in the ectodomain. All CD44 isoforms have a hyaluronic acid (HA)-binding site in the extracellular domain.