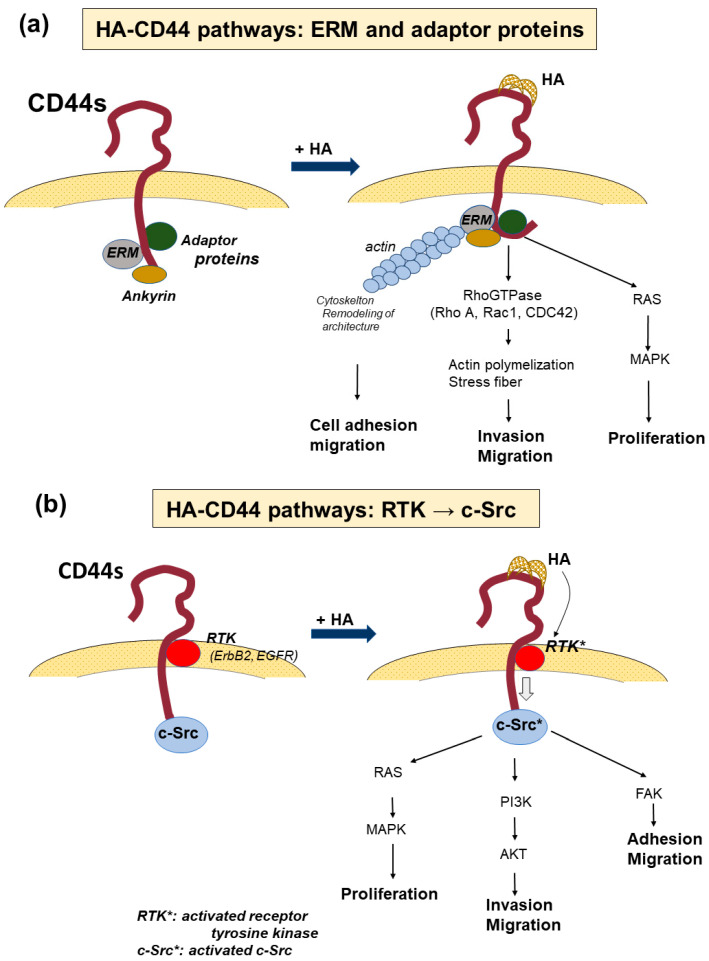
Figure 3.
The signaling pathway activated by HA-CD44 interaction. (a) The signaling pathway from the promotion of the binding of ezerin-radexin-moesin (ERM), ankyrin, and adaptor proteins to the cytoplasmic tail. Binding activates the interaction of CD44 and RAS and RhoGTPase, leading to the promotion of actin polymerization, remodeling of the cytoskeletal architectures, and facilitating cell migration and invasion. In contrast, the oncogenic gene RAS activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and promotes cell proliferation. (b) Signaling pathway activated by receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). HA-CD44 interaction activates RTKs, such as ErbB2 and EGFR, which elevate the activities of the non-receptor kinases of the Src family or Ras family GTPase. Such intracellular signaling enhances the activity of downstream signaling pathways, such as MAPK, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). The former promotes cell proliferation, while the latter two enhance cell migration and invasion. *: activated gene.