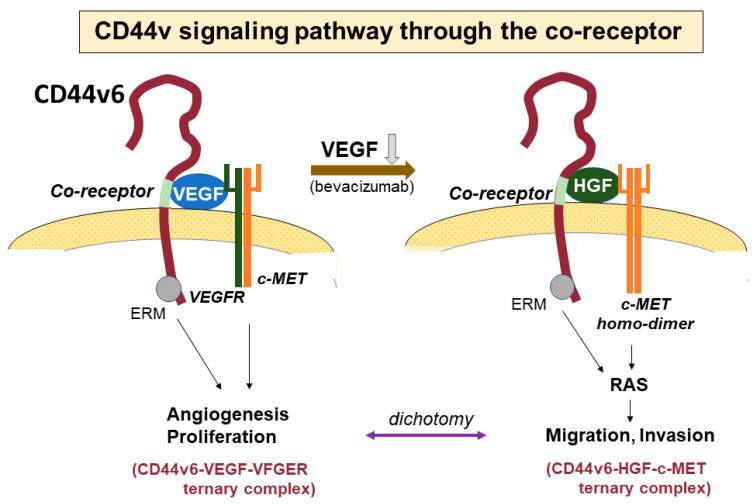
Figure 4.
The signaling pathway through co-receptors of CD44. The CD44v6 isoform has a co-receptor in the variant region of the CD44 ectodomain. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) can bind to the co-receptor. VEGF bound to the co-receptor further binds to the VEGF receptor (VEGFR), forming a ternary complex of CD44v6-VEGF-VEGFR to promote angiogenesis. VEGFR and cMET form a heterodimer and suppress migratory activity via the interaction of HGF and cMET. In contrast, the binding of VEGF to CD44 is inhibited by the anti-VEGF antibody bevacizumab, and thus, CD44v6 does not form the heterodimer of VEGFR and cMET and a homodimer with cMET is instead generated. HGF then binds to the co-receptor of CD44 instead of VEGF, creating a CD44v6-HGF-cMET ternary complex. This stimulates the Ras signaling pathway, resulting in increased motility.