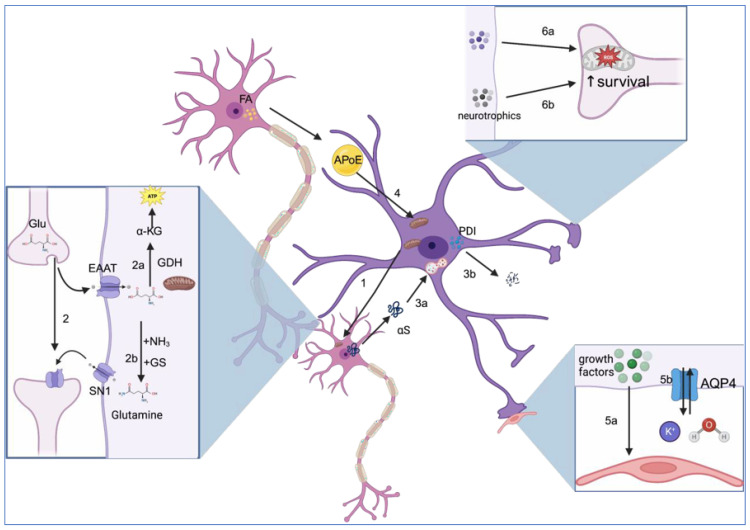
Figure 1.
Astrocytes exhibit various neuroprotective properties. (1) Healthy astrocyte mitochondria are shown to be transferred to neurons during stress, which promotes a healthy neuron function. (2) Glutamate is taken up by astrocytes via EAAT. (2a) GDH, expressed in the mitochondria, converts glutamate into α-KG, a substrate for ATP production. (2b) With the usage of ammonia, the glutamine synthetase (GS) enzyme converts glutamate into glutamine, which is taken up by neurons via the SN1 transporters. (3a) Healthy astrocytes take up extracellular αS, which is degraded by the lysosome. (3b) PDI prevents extracellular αs fibrillization. (4) Fatty acids are transported from neurons to astrocytes by ApoE and converted into energy by astrocyte mitochondria. (5a) Growth factors secreted by perivascular astrocytes regulate and promote the secretion of tight junction proteins by endothelial cells, therefore maintaining the integrity of the BBB. (5b) AQP4 channels found in the end-feet of perivascular astrocytes regulate potassium ion and water homeostasis, implicating astrocyte activity in the function of the BBB. (6a) Molecules produced by astrocytes such as glutathione prevent oxidative stress in neurons. (6b) Astrocyte-secreted neurotrophic factors such as MANF promote neuron survival. Figure created with biorender.com. Accessed on 13 August 2023.