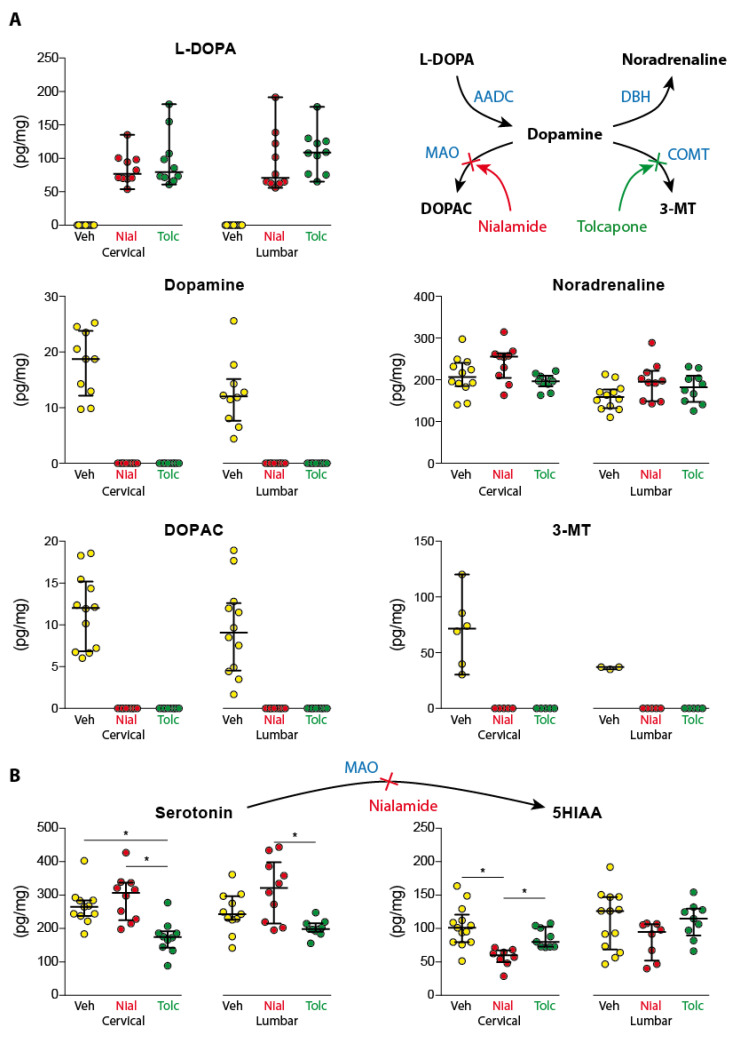
Figure 4.
Spinal content of monoamines and associated by-products following the administration of nialamide or tolcapone at the dose of 100 mg/kg. (A) Both drugs exert the same effect on the basal levels of catecholamines in the cervical and lumbar spinal cord. Both reveal the presence of endogenous L-DOPA and devrease the dopamine, DOPAC and 3-MT to levels below detection threshold. No effect is observed on noradrenaline content. (B) Nialamide slightly increases spinal levels of serotonin while decreasing the basal level of its metabolite 5HIAA. AADC: Aromatic amino-acid decarboxylase; DBH: Dopamine-β-hydroxylase; MAO: Monoamine oxidase; COMT: Catechol-O-methyltransferase; DOPAC: 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetix acid; 3-MT: 3-Methoxytyramine; 5HIAA: 5-Hydroxyindolacetic acid. * p < 0.05.